Informações básicas.
Material
Cordierite
Aplicativo
Industry, Food and Beverage, Medicine, Textile, Metallurgy
Tipo
Ceramic Filter
Filter Connector
Flat Connector
Filtration Grade
ULPA Filter
Activated Carbon Filter Type
Bulk Type
Marca registrada
SW
Pacote de transporte
Carton
Especificação
50x50x50, 100x100x50, 595x260x95
Origem
China
Código HS
3815120090
Descrição do produto
Description:;
Carrier:; Ceramic honeycomb substrate (cordierite monolith); or metal honeycomb substrate (stainless steel crust and Fe-Cr-Al honeycomb body);.;
Technical Data:;
Material:;Cordierite,; mullite ceramics
Size:;
50x50x50,;100x100x50,;595x260x95
Working Temperature:;220°C-1100°C
Channels:;Circular,; Square,; Rectangle
Cell Density:;
50-400 CPSI
Type:; Catalytic Converter
Usage:;
Catalytic Converter
Application:;Enameled wire,; paint room,; waste gas treatment industry.;
——————————————————————————————————————————————————
Regenerative Thermal/Catalytic Oxidizer (RTO/RCO); :;
Regenerated heat/catalytic oxidant (RTO/RCO);:; it is widely used in automotive coatings,; chemical industry,; electronic and electric manufacturing industry,; contact combustion system and other fields.;Ceramic honeycomb is designated as a structural regenerative medium for RTO/RCO.;
Advantage:;
1.; Various materials and specifications
2.; Products with different formulas can be customized according to customer requirements.;
3.; Small resistance loss
4.; Low thermal expansion coefficient
5.; Excellent crack resistance
6.; It can be customized to meet the emission standards of different countries.;
Aplicativos:;
1.; It can be used as a heat exchanger in the RTO of the heat recovery device.;
2.; Can be used as a catalyst to purify automobile exhaust and motorcycle exhaust to remove odor.;
3.; Applicable to food service industry,; environmental protection industry,; metallurgy industry,; etc
Test Equipment:;
Particle size distribution tester
Aperture and specific surface meter
Metal distribution,; crystalline structure
Catalyst activity evaluation system
Production Equipment:;
Coating continuous microwave drying system
Slurry nanometer grinding preparation system
Slurry quantitative spraying system
RFQ:;
Q:;Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A:;We are professional manufacturer which has almost 20 years of experience in this industry.;
Q:;Can you produce according to the samples?
A:;Yes,;we can produce by your samples or technical drawings.;
Q:;Would it be possible for us to visit your factory?
A:;Sure,;we welcomed our customers visit our factory in any time.;
Q:;Will your company supply samples?
A:;Yes,;the sample expense will be deducted from the value of your order.;
Q:;What’s your payment terms?
A:;T/T,; L/C,; Western Union,; Money Gram,; are available for us.;
Q:;Delivery time for my order?
A:;Within 7-15 working days for your sample order; 20 working days for your bulk order( It depends on the models and quantity you are going to order);.;
Address: Room. 3902-2 TianAn CHINAMFG Town No. 228 Ling Lake Avenue, New Wu District, HangZhou City, ZheJiang Province, China.
Business Type: Manufacturer/Factory, Group Corporation
Business Range: Auto, Motorcycle Parts & Accessories, Chemicals, Industrial Equipment & Components, Manufacturing & Processing Machinery
Management System Certification: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 20000, IATF16949
Main Products: Honeycomb Catalytic, Three Way Catalytic, Chemical Catalytic, Exhaust Filter, Industrial Catalytic
Company Introduction: Established in 2003, Sheung Well International Corp. Is a professional enterprise specialized in developing, manufacturing, selling automotive vehicles, Universal fuel engine and industrial three-way catalyst and converters, four-way converters. With independent intellectual property rights, its technology has been approved by ISO9001, TS16949 quality and management systems.
Sheung Well is an all-round designer and manufacturer who has a innovative and quality managing team mainly consists of doctorates and masters. Based on its cutting edge technology, rich experience and modern production and quality management skills, CHINAMFG is providing customers with first-class products and services.
Oriented in market, with innovation as its soul, centralized in serving the society, CHINAMFG lays emphasis on developing technology and products of controlling Exhaust emissions and other industrial catalysts. By providing customers with technology and supports of new products, it is committed to becoming the word-class all-around enterprise in catalyst circle from home and abroad.
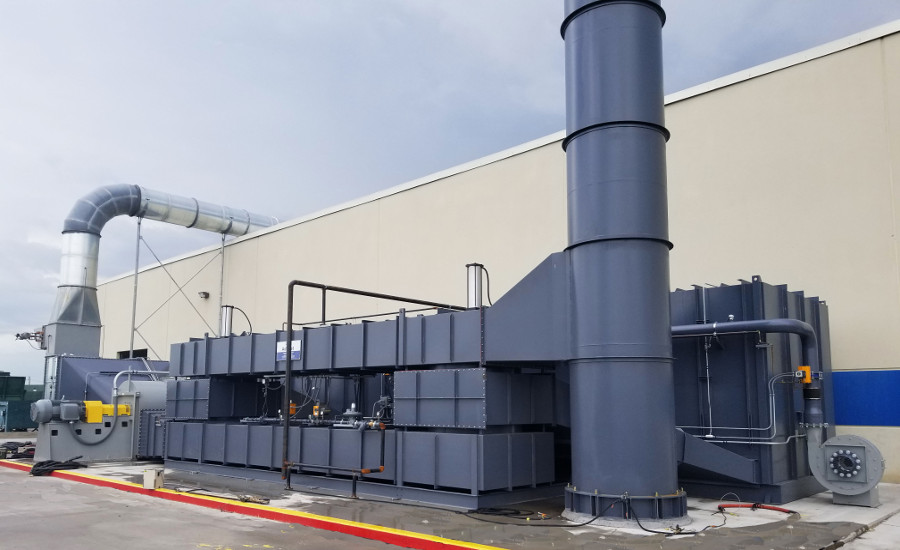

Qual é a diferença entre um oxidante térmico regenerativo e um oxidante térmico?
Um oxidador térmico regenerativo (RTO) e um oxidador térmico são tipos de dispositivos de controle de poluição do ar usados para o tratamento de compostos orgânicos voláteis (VOCs) e outros poluentes do ar. Embora tenham a mesma finalidade, há diferenças distintas entre as duas tecnologias.
Aqui estão as principais diferenças entre um oxidante térmico regenerativo e um oxidante térmico:
- Princípio de funcionamento: A diferença fundamental está no princípio de operação. Um oxidador térmico opera usando apenas a alta temperatura para oxidar e destruir os poluentes. Normalmente, ele depende de um queimador ou de outras fontes de calor para elevar a temperatura dos gases de escape até o nível necessário para a combustão. Em contrapartida, um RTO utiliza um sistema de trocador de calor regenerativo para pré-aquecer os gases de escape de entrada, capturando e transferindo o calor dos gases de saída. Esse mecanismo de troca de calor melhora significativamente a eficiência energética geral do sistema.
- Recuperação de calor: A recuperação de calor é uma característica distintiva de um RTO. O trocador de calor regenerativo em uma RTO permite a recuperação de uma quantidade significativa de calor dos gases de saída. Esse calor recuperado é então usado para pré-aquecer os gases de entrada, reduzindo o consumo de energia do sistema. Em um oxidador térmico típico, a recuperação de calor é limitada ou inexistente, resultando em requisitos de energia mais altos.
- Eficiência energética: Devido ao mecanismo de recuperação de calor, os RTOs geralmente são mais eficientes em termos de energia em comparação com os oxidantes térmicos tradicionais. O trocador de calor regenerativo em um RTO permite eficiências térmicas de 95% ou mais, o que significa que uma parte significativa da entrada de energia é recuperada e utilizada no sistema. Os oxidantes térmicos, por outro lado, normalmente têm eficiências térmicas mais baixas.
- Custos operacionais: A maior eficiência energética dos RTOs se traduz em custos operacionais mais baixos a longo prazo. O consumo reduzido de energia pode resultar em uma economia significativa nas despesas com combustível ou eletricidade em comparação com os oxidantes térmicos. No entanto, o investimento de capital inicial de um RTO é geralmente maior do que o de um oxidante térmico devido à complexidade do sistema de trocador de calor regenerativo.
- Controle de concentrações de poluentes: Os RTOs são mais adequados para lidar com concentrações variáveis de poluentes em comparação com os oxidantes térmicos. O sistema de trocador de calor regenerativo em um RTO permite melhor controle e ajuste dos parâmetros operacionais para acomodar as flutuações nas concentrações de poluentes. Os oxidadores térmicos normalmente são menos adaptáveis a cargas variáveis de poluentes.
Em resumo, as principais diferenças entre um oxidante térmico regenerativo e um oxidante térmico estão no princípio operacional, nos recursos de recuperação de calor, na eficiência energética, nos custos operacionais e no controle das concentrações de poluentes. Os RTOs oferecem maior eficiência energética, melhor controle das concentrações de poluentes e menores custos operacionais, mas exigem um investimento inicial maior em comparação com os oxidantes térmicos tradicionais.
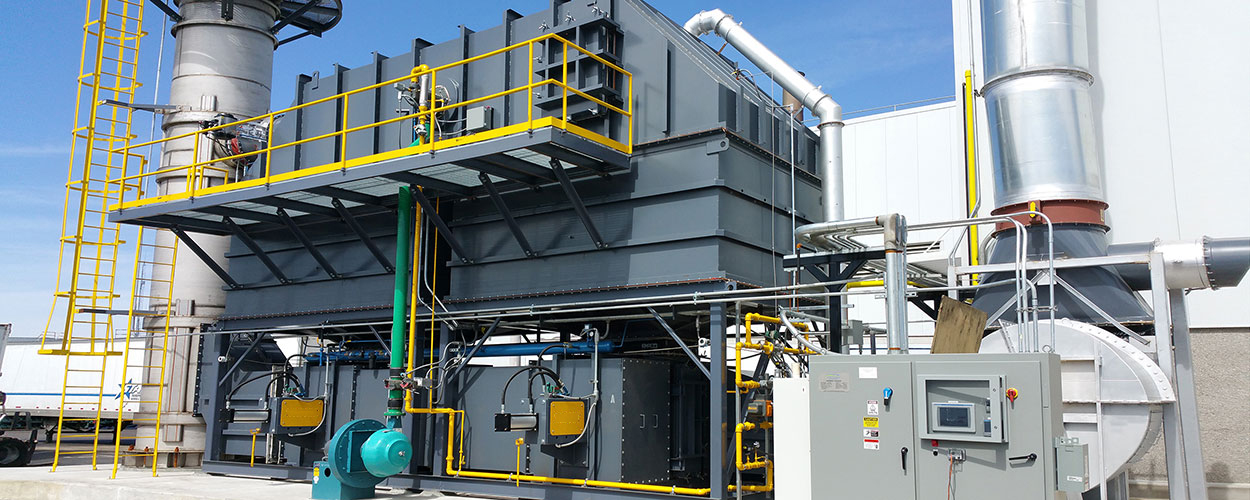

Can regenerative thermal oxidizers handle high-temperature exhaust streams?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are designed to handle high-temperature exhaust streams efficiently. They are capable of accommodating exhaust gases with elevated temperatures and effectively treating them for pollutant removal. Here are some key points regarding the handling of high-temperature exhaust streams in RTOs:
- Thermal Stability: RTOs are constructed using materials that can withstand high temperatures, typically ranging from 800 to 1,500 degrees Celsius (1,472 to 2,732 degrees Fahrenheit). The combustion chamber, heat exchangers, and other components are designed to maintain their structural integrity and thermal stability under these conditions.
- Recuperação de calor: One of the primary advantages of RTOs is their ability to recover and reuse heat from the high-temperature exhaust streams. The heat exchangers within the RTO capture the thermal energy from the outgoing exhaust gases and transfer it to the incoming process air or gas stream. This heat recovery process improves the overall energy efficiency of the system and reduces the need for additional fuel consumption.
- Effective Combustion: RTOs are equipped with combustion chambers where the high-temperature exhaust gases are directed. In the combustion chamber, the pollutants in the exhaust stream are oxidized at high temperatures, typically above the autoignition temperature of the pollutants. This ensures effective destruction of the pollutants, even in high-temperature environments.
- Heat Exchange: RTOs utilize a regenerative heat exchange system, which allows for the efficient transfer of heat between the incoming and outgoing gas streams. The heat exchange media within the RTO alternately absorbs and releases heat, enabling the preheating of the incoming gases and cooling of the outgoing gases. This heat exchange process helps maintain the desired operating temperatures within the RTO while maximizing energy recovery.
- System Design Considerations: When handling high-temperature exhaust streams, proper system design is crucial. Factors such as the choice of materials, insulation, and thermal expansion considerations are taken into account to ensure safe and efficient operation at elevated temperatures. Additionally, temperature monitoring and control systems are implemented to maintain optimal operating conditions.
It is important to note that the specific temperature limits and capabilities of an RTO may vary depending on the design, materials used, and the specific requirements of the application. Consulting with experienced engineers or RTO manufacturers can provide valuable insights into the suitability of an RTO for handling a particular high-temperature exhaust stream.
Overall, RTOs are well-suited for handling high-temperature exhaust streams, offering effective pollutant destruction, heat recovery, and energy efficiency in industrial applications.
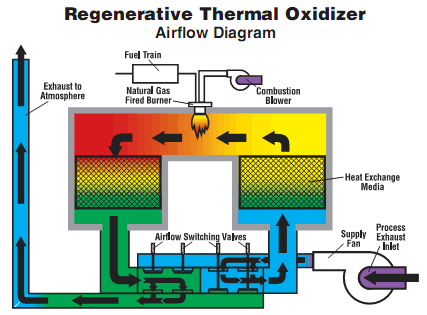
Como funciona um oxidante térmico regenerativo?
Um oxidante térmico regenerativo (RTO) é um dispositivo avançado de controle de poluição do ar que opera por meio de um processo cíclico para remover compostos orgânicos voláteis (VOCs), poluentes atmosféricos perigosos (HAPs) e outros contaminantes transportados pelo ar dos gases de exaustão. Aqui está uma explicação detalhada de como um RTO funciona:
1. Pleno de entrada: Os gases de escape contendo poluentes entram no RTO através do plenum de admissão.
2. Leitos de troca de calor: O RTO contém vários leitos de trocadores de calor preenchidos com meios de armazenamento de calor, tipicamente materiais cerâmicos ou empacotamento estruturado. Os leitos de trocadores de calor são dispostos em pares.
3. Válvulas de controle de fluxo: As válvulas de controle de fluxo direcionam o fluxo de ar e controlam a direção dos gases de escape através do RTO.
4. Câmara de combustão: Os gases de exaustão, agora direcionados para a câmara de combustão, são aquecidos a uma alta temperatura, tipicamente entre 1400°F (760°C) e 1600°F (870°C). Essa faixa de temperatura garante oxidação térmica efetiva dos poluentes.
5. Destruição de COV: A alta temperatura na câmara de combustão faz com que os VOCs e outros contaminantes reajam com o oxigênio, resultando em sua decomposição térmica ou oxidação. Esse processo decompõe os poluentes em vapor de água, dióxido de carbono e outros gases inofensivos.
6. Recuperação de calor: Os gases quentes e purificados que saem da câmara de combustão passam pelo plenum de saída e fluem pelos leitos do trocador de calor que estão na fase oposta de operação. O meio de armazenamento de calor nos leitos absorve o calor dos gases de saída, o que pré-aquece os gases de exaustão de entrada.
7. Troca de ciclo: Após um intervalo de tempo específico, as válvulas de controle de fluxo trocam a direção do fluxo de ar, permitindo que os leitos do trocador de calor que estavam pré-aquecendo os gases de entrada agora recebam os gases quentes da câmara de combustão. O ciclo então se repete, garantindo uma operação contínua e eficiente.
Vantagens de um oxidante térmico regenerativo:
Os RTOs oferecem diversas vantagens no controle da poluição do ar industrial:
1. Alta eficiência: Os RTOs podem atingir altas eficiências de destruição, normalmente acima de 95%, removendo efetivamente uma ampla gama de poluentes.
2. Recuperação de energia: O mecanismo de recuperação de calor em RTOs permite economias significativas de energia. O pré-aquecimento dos gases de entrada reduz o consumo de combustível necessário para a combustão, tornando os RTOs energeticamente eficientes.
3. Custo-efetividade: Embora o investimento de capital inicial para um RTO possa ser significativo, a economia de custos operacionais a longo prazo por meio da recuperação de energia e altas eficiências de destruição o tornam uma solução econômica ao longo da vida útil do sistema.
4. Conformidade ambiental: Os RTOs são projetados para atender a regulamentações rigorosas de emissões e ajudar as indústrias a cumprir os padrões e licenças de qualidade do ar.
5. Versatilidade: Os RTOs podem lidar com uma ampla gama de volumes de exaustão de processo e concentrações de poluentes, tornando-os adequados para diversas aplicações industriais.
No geral, um oxidante térmico regenerativo opera utilizando recuperação de calor, combustão de alta temperatura e controle de fluxo cíclico para oxidar poluentes de forma eficaz e atingir altas eficiências de destruição, minimizando o consumo de energia.

editor by CX 2024-01-30
