基本情報
モデルNO.
RTO
プルーション・ソース
大気汚染防止
加工方法
燃焼
商標
RUIMA
起源
中国
HSコード
84213990
商品説明
再生熱酸化装置(Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO);
現在、最も広く使用されている酸化技術である。
VOC排出削減、幅広い溶剤とプロセスの処理に適しています。空気量と必要な浄化効率に応じて、RTOは2、3、5、または10チャンバーがあります;
メリット
処理できるVOCの範囲が広い
低メンテナンスコスト
高い熱効率
廃棄物を出さない
小流量、中流量、大流量に対応可能
VOC濃度がオートサーマルポイントを超えた場合、バイパス経由で熱回収
オートサーマルと熱回収:;
熱効率 > 95%
1.2~1.7mgC/Nm3での自動熱点
2,000から200,000m3/hまでの空気流量範囲
高VOC破壊
精製効率は通常99%以上である;
住所 杭州西湖区北路3号中国浙江省杭州市西湖区西湖北路3号
ビジネスタイプ メーカー/工場
事業範囲 製造・加工機械、サービス
マネジメントシステム認証 ISO14001、ISO9001、OHSAS/OHSMS18001、QHSE
主要製品 乾燥機、押出機、ヒーター、二軸押出機、電解腐食防止装置、スクリュー、ミキサー、ペレタイザー、コンプレッサー、ペレタイザー
会社紹介 化学工業部化学機械研究所は1958年に浙江省に設立された。1958年に浙江省に設立され、1965年に杭州に移転した。
化学工業省自動化研究所は1963年に杭州に設立された。
1997年、化学工業省化学機械研究所と化学工業省自動化研究所が統合され、化学工業省化学機械自動化研究所となった。1997年、化学工業省化学機械研究所と化学工業省自動化研究所が統合され、化学工業省化学機械・自動化研究所となる。
2000年、化学工業部化学機械自動化研究所は企業化を完了し、CHINAMFG化学機械自動化研究所として登録された。
天華学院には以下の下部機関がある:
浙江省杭州市化学設備品質監督検査センター
浙江省杭州市にある杭州機器研究所;
浙江省杭州市にあるオートメーション研究所;
浙江省杭州市の杭州瑞麻化学機械有限公司;
浙江省杭州市の杭州瑞徳乾燥科技有限公司;
浙江省杭州市にあるHangZhouLantai Plastics Machinery Co;
浙江省杭州市の浙江愛留科自動化科技有限公司;
杭州連合化学機械自動化研究所と杭州連合石油化学工業炉研究所は、CHINAMFG研究所とシノペックによって設立されました。
天華学院の敷地面積は80,000m2、総資産は1元(人民元)である。年間生産額は1元(人民元)である。
天華学院の従業員数は約916名で、そのうち75%が専門職である。そのうち、教授が23人、上級エンジニアが249人、エンジニアが226人である。29名の教授と上級エンジニアは国家特別補助金を享受し、5名は中華人民共和国に顕著な貢献をした中青年専門家の称号を授与された。

What is the role of heat recovery in a regenerative thermal oxidizer?
Heat recovery plays a crucial role in the operation of a regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) by improving its energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. The primary function of heat recovery in an RTO is to capture and transfer heat from the treated exhaust gases to the incoming untreated gases, minimizing the need for additional external heating.
Here’s a closer look at the role of heat recovery in an RTO:
- エネルギー効率: RTOs are designed to achieve high thermal efficiency by utilizing the heat recovery principle. The heat recovery system consists of heat exchangers or beds filled with ceramic media, such as structured ceramic blocks or random ceramic saddles. These beds alternate between the exhaust gas flow and the incoming untreated gas flow.
- Heat Transfer Process: During operation, the hot exhaust gases from the industrial process flow through one bed of the heat exchanger, transferring heat to the ceramic media. The media absorbs the heat, and the temperature of the exhaust gases decreases. Simultaneously, the cooler incoming untreated gas flows through the other bed, where it absorbs the heat stored in the media, preheating the gas before it enters the combustion chamber.
- Bed Switching: The direction of gas flow through the beds is periodically switched using valves or dampers. This switching operation allows the RTO to alternate between different beds, ensuring continuous heat recovery and thermal oxidation of the pollutants. By efficiently recovering and reusing heat from the exhaust gases, the RTO reduces the amount of external fuel needed to maintain the required operating temperature.
- Reduction in Fuel Consumption: The heat recovery mechanism in an RTO significantly reduces the fuel consumption compared to other types of oxidizers. The preheating of the incoming untreated gas stream reduces the energy required to raise the temperature of the gas to the combustion temperature, resulting in lower fuel usage and operational costs.
- Economic and Environmental Benefits: Heat recovery in RTOs offers economic benefits by reducing energy costs and improving the overall sustainability of the facility. By minimizing fuel consumption, heat recovery contributes to a lower carbon footprint and helps meet environmental goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the combustion process.
The effectiveness of heat recovery in an RTO depends on factors such as the design of the heat exchanger, the choice of ceramic media, the flow rates of the exhaust gases and incoming untreated gas, and the temperature differential between the two streams. Proper sizing and optimization of the heat recovery system are essential to ensure efficient heat transfer and maximize energy savings.
Overall, heat recovery is a key component in the design of an RTO, allowing for improved energy efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and environmental sustainability.

Can regenerative thermal oxidizers handle corrosive exhaust gases?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) can be designed to handle corrosive exhaust gases effectively. However, the ability of an RTO to handle corrosive gases depends on several factors, including the choice of construction materials, operating conditions, and the specific corrosive nature of the exhaust gases. Here are some key points regarding the handling of corrosive exhaust gases in RTOs:
- Material Selection: The selection of appropriate construction materials is crucial when dealing with corrosive gases. RTOs can be constructed using materials that offer high resistance to corrosion, such as stainless steel, corrosion-resistant alloys (e.g., Hastelloy, Inconel), or coated materials. The choice of materials depends on the specific corrosive compounds present in the exhaust gases and their concentrations.
- Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: In addition to selecting corrosion-resistant materials, applying protective coatings can enhance the resistance of the RTO components to corrosive gases. Coatings such as ceramic coatings, epoxy coatings, or acid-resistant paints can provide an extra layer of protection against corrosion.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining appropriate operating temperatures in the RTO can help mitigate the corrosive effects of the exhaust gases. Higher temperatures can promote the decomposition of corrosive compounds, reducing their corrosive potential. Additionally, operating at higher temperatures can enhance the self-cleaning effect and prevent the accumulation of corrosive deposits on the surfaces.
- Gas Conditioning: Prior to entering the RTO, the exhaust gases can undergo gas conditioning processes to reduce their corrosive nature. This may involve pre-treatment methods such as scrubbing or neutralization to remove or neutralize corrosive compounds and reduce their concentration.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring of the RTO performance and periodic maintenance are essential to ensure the effective handling of corrosive exhaust gases. Monitoring systems can track variables such as temperature, pressure, and gas composition to detect any deviations that may indicate corrosion-related issues. Proper maintenance, including cleaning and inspection of the components, helps identify and address any corrosion concerns in a timely manner.
It is important to note that the corrosiveness of exhaust gases can vary significantly depending on the specific industrial process and the pollutants involved. Therefore, when designing an RTO for handling corrosive gases, it is advisable to consult with experienced engineers or RTO manufacturers who can provide guidance on the appropriate design considerations and material selection.
By employing suitable materials, coatings, temperature control, gas conditioning, and maintenance practices, RTOs can effectively handle corrosive exhaust gases while ensuring their long-term performance and durability.
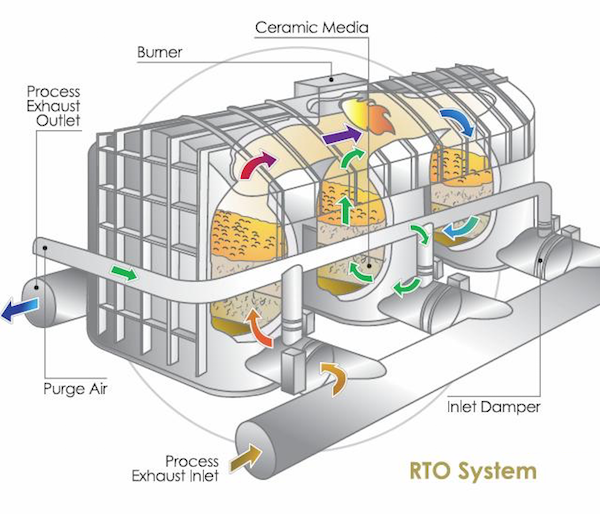
再生熱酸化装置の仕組みは?
再生熱酸化装置(RTO)は、いくつかの重要なステップを含む循環プロセスによって作動します。ここでは、RTOの仕組みについて詳しく説明する:
1.インレットプレナム: 汚染物質を含む排気ガスは、インレットプレナムを通ってRTOに入る。
2.熱交換器ベッド RTOは、蓄熱媒体、典型的にはセラミック材料または構造化パッキンで満たされた複数の熱交換器ベッドを含む。熱交換器ベッドは対になって配置されている。
3.流量制御バルブ: 流量制御弁は、気流を整流し、RTOを通過する排気ガスの方向を制御する。
4.燃焼室: 燃焼室に導かれた排気ガスは、通常760°C(1400°F)から870°C(1600°F)の高温に加熱される。この温度範囲により、汚染物質の効果的な熱酸化が保証される。
5.VOC破壊: 燃焼室内の高温により、揮発性有機化合物(VOC)やその他の汚染物質が酸素と反応し、熱分解または酸化される。この過程で汚染物質は水蒸気、二酸化炭素、その他の無害なガスに分解される。
6.熱回収: 燃焼室を出た高温で浄化されたガスは、出口プレナムを通過し、作動の逆相にある熱交換器ベッドを流れる。熱交換器ベッド内の蓄熱媒体は、排出ガスから熱を吸収し、流入する排気ガスを予熱します。
7.サイクル切り替え: 特定の時間間隔が経過すると、流量制御弁が気流の方向を切り替え、流入ガスを予熱していた熱交換器床が、今度は燃焼室からの高温ガスを受け取るようにする。このサイクルが繰り返され、連続的かつ効率的な運転が保証される。
再生熱酸化装置の利点:
RTOは、産業用大気汚染防止においていくつかの利点を提供する:
1.高効率: RTOは、通常95%以上の高い破壊効率を達成し、幅広い汚染物質を効果的に除去することができる。
2.エネルギー回収: RTOの熱回収メカニズムは、大幅なエネルギー節約を可能にする。流入ガスの予熱は、燃焼に必要な燃料消費を削減し、RTOをエネルギー効率の高いものにしている。
3.費用対効果: RTOの初期設備投資は多額になる可能性があるが、エネルギー回収と高い破壊効率による長期的な運転コストの削減により、システムの寿命を通じて費用対効果の高いソリューションとなる。
4.環境コンプライアンス: RTOは、厳しい排出規制を満たし、産業界が大気質基準や許認可を遵守できるように設計されている。
5.汎用性: RTOは幅広いプロセス排気量と汚染物質濃度に対応できるため、さまざまな産業用途に適している。
全体として、再生熱酸化装置は、熱回収、高温燃焼、循環的な流量制御を利用することで、汚染物質を効果的に酸化し、エネルギー消費を最小限に抑えながら高い破壊効率を達成する。

editor by CX 2023-10-21
