基本訊息
類型
環境監測儀器
主要功能
廢氣去除
應用
化工
品牌
雷德桑特
清潔效率
99.8%
狀態
新的
商標
雷德桑特
運輸套餐
薄膜包裹
起源
中國 浙江
產品描述
杭州瑞德森機械有限公司;,;有限公司;專業開發製造創新粉末冷卻造粒機械及相關工業廢氣處理設備。具有近20年的生產歷史;我們在中國20多個省份擁有良好的市場;部分產品出口沙烏地阿拉伯、新加坡、墨西哥、巴西,;西班牙,;美國,;俄羅斯和韓國; ETC。
規格:;
* 比現有設施更緊湊
* 營運成本低
* 設施使用壽命長
* 壓力無變化
目的:;
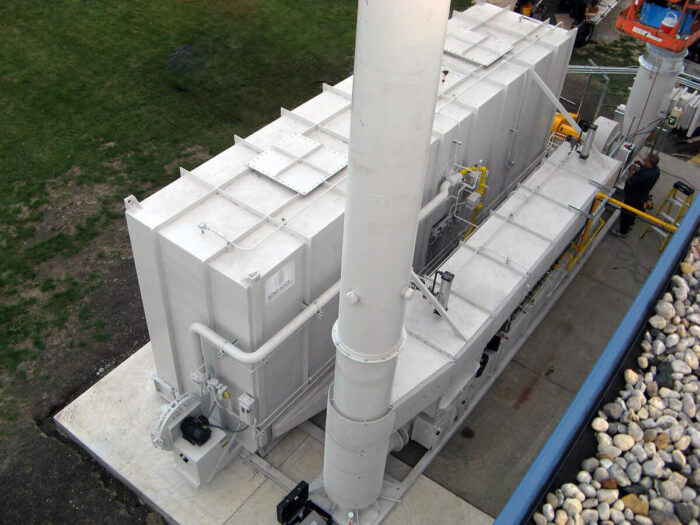
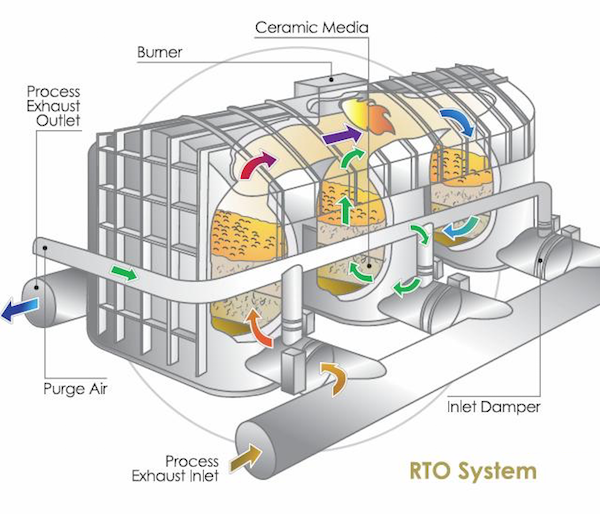
燃燒揮發性有機化合物(VOC)的節能係統;利用熱量產生廢氣;採用陶瓷蓄熱材料(催化劑)收集99.;8%以上的廢氣餘熱;表面積大,壓力損失低;
應用:;
1.;塗裝乾燥工藝
2.;金屬印刷工藝
3.;纖維乾燥過程
4.;膠帶工藝
5.;廢棄物處理工藝
6.;半導體製造工藝
7.;抽煙,;糖果和烘焙過程
8.;石化過程;
9.;醫藥和食品製造過程;
10.;其他VOC產生過程
優點:;
* 比現有設施更緊湊
* 壓力無變化
* 熱回收率高(95%以上);
* 完善的VOC處理(99.;8%以上);
* 設施使用壽命長
* 營運成本低
* 可製作圓形或四邊形
一般描述與特點:;
1.;工作原理
透過旋轉旋轉閥連續改變流量的操作方法
2.;過程壓力變化
由於旋轉閥的旋轉,風向會發生順序變化,因此壓力不會變化
3.;投資成本
約 70% 的床型
4.;安裝空間
它是單一容器,因此結構緊湊,需要的安裝空間較小。
5.;維護
由於旋轉閥是唯一的 1 個移動部件,因此易於維護。
旋轉閥由於旋轉速度低,密封件很少磨損;
6.;穩定
在此過程中沒有風險,因為即使旋轉閥出現故障,它也始終打開。
7.;處理效率
即使長時間運行,密封件也很少磨損,處理效率得以維持;
地址:浙江省杭州市經濟開發區振新中路3號
業務類型: 製造商/工廠, 貿易公司
業務範圍:化工、電氣電子、製造加工機械、安全防護
管理系統認證:ISO 9001
主要產品:造粒機、刨片機、造粒機、造粒機、化學造粒機、Vocs
公司簡介:杭州瑞德森機械有限公司,前身為杭州新特塑膠機械廠,是一家專業生產創新塑膠回收機械的企業。憑藉近20年的經驗,我們在國內20個省市自治區擁有良好的市場,部分產品出口到印尼、俄羅斯、越南等。管材撕碎回收生產線、連續退火鍍錫機、QX型PET、PE及皮殼清洗生產線、SDP雙軌塑膠回收破碎機、SJ熱切造粒機組、PVC管(五葉)生產線、PVC異型材產品門窗生產線、水中顆粒生產線以及塑膠和回收粉碎機。我們獲得了5項技術專利。
本公司注重技術改造,引進國內外先進技術,不斷開發新產品。我們的宗旨是挑戰高品質,提供最好的產品。我們正在努力實現我們的口號。讓客戶滿意是我們永恆的追求。
我們正在尋找海外客戶或代理商。如果您對我們的提案感興趣,請讓我們知道我們的哪種產品最有可能吸引您或您的客戶。如果您能給我們一些關於我們產品的市場前景的想法,我們將不勝感激。我們希望盡快收到您的有利訊息!我們的目標是希望現在或不久的將來能與您建立良好的關係。如果您有任何問題或要求,請隨時與我們聯繫。
我們也真誠歡迎您來本公司洽談業務、洽談業務。為進一步拓展市場與客戶,本公司以全新的經營理念-品質、榮譽、服務,以全新的品牌姿態迎接國內外客戶。我們正在尋找 ISO 90001 管理品質系統來滿足客戶的要求!

What are the limitations of regenerative thermal oxidizers?
While regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are widely used for air pollution control, they do have certain limitations that should be considered. Here are some key limitations of RTOs:
- High Capital Cost: RTOs typically have higher capital costs compared to other air pollution control technologies. The complexity of the regenerative heat exchanger system, which enables high energy efficiency, can contribute to the higher upfront investment required for RTO installation.
- Space Requirements: RTOs generally require a larger footprint compared to some other air pollution control devices. The presence of regenerative heat exchangers, combustion chambers, and associated equipment necessitates adequate space for installation. This can be a limitation for industries with limited available space.
- High Energy Consumption during Startup: RTOs require a certain amount of time and energy to reach their optimal operating temperature during startup. This initial energy consumption can be relatively high, and it is important to consider this aspect when planning the operational schedule and energy management of an RTO system.
- Limitations in Handling Low Concentration VOCs: RTOs may have limitations in effectively treating low concentration volatile organic compounds (VOCs). If the VOC concentrations in the exhaust gas are too low, the energy required to maintain the necessary temperature for oxidation may be higher than the energy released during the combustion process. In such cases, other air pollution control technologies or pre-concentration techniques may be more suitable.
- Particulate Matter Control: RTOs are not specifically designed for controlling particulate matter emissions. While they may provide some incidental removal of fine particulate matter, their removal efficiency for particulates is generally lower compared to dedicated particulate control devices such as fabric filters (baghouses) or electrostatic precipitators.
- Chemically Corrosive Gases: RTOs may not be suitable for treating exhaust gases containing highly corrosive compounds. The high temperatures within the RTO can accelerate corrosion of materials, and the presence of corrosive gases may require additional corrosion-resistant materials or alternative air pollution control technologies.
Despite these limitations, RTOs remain an effective and widely used technology for the destruction of gaseous pollutants in various industrial applications. It is important to evaluate the specific requirements, characteristics of the exhaust gases, and environmental regulations when considering the implementation of an RTO system.
再生熱氧化器與生物過濾器的性能相比如何?
蓄熱式熱氧化器(RTO)和生物過濾器都是廣泛使用的空氣污染物處理技術,但它們的工作原理和性能特徵有所不同。以下是 RTO 和生物過濾器的性能比較:
| 性能方面 | 蓄熱式熱氧化器 (RTO) | 生物過濾器 |
|---|---|---|
| 排放去除效率 | RTO 在去除揮發性有機化合物 (VOC) 和有害空氣污染物 (HAP) 方面非常有效率。他們對這些污染物的破壞效率可達 95% 以上。 | 生物過濾器還有可能對某些揮發性有機化合物和有氣味的化合物實現高去除效率。然而,它們的性能可能會根據生物過濾器中的特定污染物和微生物活性而變化。 |
| 適用性 | RTO 用途廣泛,可以處理多種污染物,包括 VOC、HAP 和有味化合物。它們非常適合高流量和高污染物濃度。 | 生物過濾器在處理有氣味的化合物和某些揮發性有機化合物方面特別有效。它們通常用於廢水處理設施、堆肥作業和農業設施等應用。 |
| 能源消耗 | RTO 需要大量能量才能達到並維持氧化的高工作溫度。它們依靠燃料燃燒或外部熱源來獲取所需的熱能。 | 生物過濾器被認為是低能耗系統,因為它們依靠微生物的自然生物活性來分解污染物。它們通常不需要外部加熱或燃料消耗。 |
| 維護 | RTO 通常需要定期維護和監控以確保正常運作。這包括檢查、熱交換介質的清潔以及組件的潛在維修或更換。 | 生物過濾器需要定期維護以優化其性能。這可能涉及監測和調整濕度水平、控制溫度以及偶爾更換過濾介質或添加微生物接種劑。 |
| 資本和營運成本 | 與生物過濾器相比,RTO 由於其複雜的設計、專用材料和能源密集型操作,通常具有更高的資本成本。營運成本包括燃料消耗或暖氣用電。 | 與 RTO 相比,生物過濾器的資本成本通常較低。它們設計更簡單,並且不需要燃料消耗。然而,營運成本可能包括定期更換過濾介質和潛在的氣味控制措施。 |
值得注意的是,選擇合適的技術取決於多種因素,例如待處理的特定污染物、製程條件、監管要求和特定場地的考慮因素。諮詢環境工程師或空氣污染控制專家可以幫助確定最適合特定應用的技術。
綜上所述,RTO 和生物過濾器具有不同的性能特徵,RTO 具有去除效率高、通用性強、適合高流量和高濃度應用的優點,而生物過濾器對有氣味的化合物有效,能耗低,且資本通常較低成本。
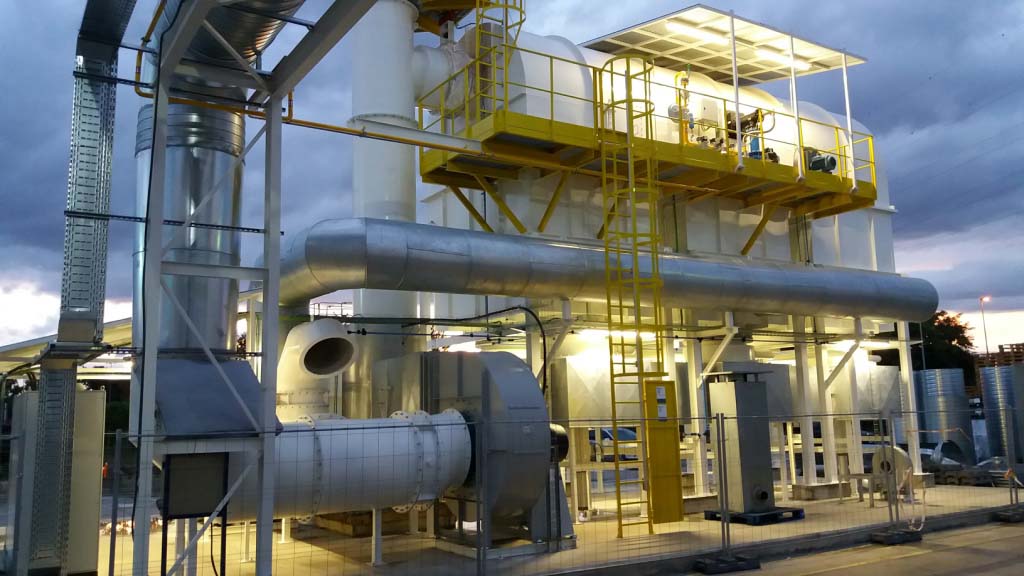

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers handle start-up and shutdown procedures?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) have specific procedures for start-up and shutdown to ensure safe and efficient operation. These procedures are designed to optimize the performance of the RTO and minimize any potential risks. Here is an overview of how RTOs handle start-up and shutdown:
- Start-up Procedure: During start-up, the RTO goes through a series of steps to reach its operating temperature. The start-up procedure typically involves the following stages:
- Purge Stage: The RTO is purged with clean air or an inert gas to remove any potential flammable or explosive gases that may have accumulated during the shutdown period.
- Preheat Stage: The RTO’s heat exchangers are preheated using a burner or an auxiliary heat source. This gradually increases the temperature of the heat exchange media (typically ceramic or metallic beds) and the combustion chamber.
- Heat Soak Stage: Once the heat exchangers reach a certain temperature, the RTO enters the heat soak stage. In this stage, the heat exchangers are fully heated, and the RTO operates in a self-sustaining mode, with the combustion chamber temperature being maintained primarily by the heat released from the oxidation of pollutants in the exhaust gas.
- Normal Operation: After the heat soak stage, the RTO is considered to be in normal operation mode, where it maintains the desired operating temperature and treats the exhaust gas containing pollutants.
- Shutdown Procedure: The shutdown procedure of an RTO is aimed at safely and efficiently stopping the operation of the system. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Cool Down: The RTO is gradually cooled down by reducing the flow of the exhaust gas and the supply of combustion air. This helps to prevent thermal stress on the equipment and minimize the risk of fires or other safety hazards.
- 熱回收: During the cool-down phase, the RTO may employ heat recovery techniques to capture and utilize the residual heat for other purposes, such as preheating incoming process air or water.
- Purge: Once the RTO has cooled down sufficiently, a purge cycle is initiated to remove any residual gases or contaminants from the system. This helps to ensure a clean and safe environment for maintenance activities or subsequent start-ups.
- Complete Shutdown: After the purge cycle, the RTO is considered to be in a fully shut-down state, and it can remain in this state until the next start-up is initiated.
It is important to note that the specific start-up and shutdown procedures for an RTO may vary depending on the design and manufacturer. Manufacturers typically provide detailed guidelines and instructions for operating their specific RTO models, and it is crucial to follow these guidelines to ensure safe and efficient operation.

編輯:夢想 2024-05-16
