Informações básicas.
Modelo NO.
RTO incrível
Tipo
Incinerador
Economia de energia
100
Fácil de operar
100
Alta eficiência
100
Menos manutenção
100
Marca registrada
Fantástico
Pacote de transporte
Madeira no exterior
Especificação
180*24
Origem
China
Código HS
8416100000
Descrição do produto
RTO
Oxidador térmico regenerativo
Compared with traditional catalytic combustion,; direct thermal oxidizer,; RTO has the merits of high heating efficiency,; low operation cost,; and the ability to treat large flux low concentration waste gas.; When VOCs concentration is high,; secondary heat recycle can be realized,; which will greatly reduce the operation cost.; Because RTO can preheat the waste gas by levels through ceramic heat accumulator,; which could make the waste gas to be completely heated and cracked with no dead corner(treatment efficiency>99%);,;which reduce the NOX in the Exhausting gas,; if the VOC density >1500mg/Nm3,; when the waste gas reach cracking area,; it has been heated up to cracking temperature by heat accumulator,; the burner will be closed under this condition.;
RTO can be devided into chamber type and rotary type according to difference operation mode.; Rotary type RTO has advantages in system pressure,; temperature stability,; investment amount,; etc
Recuperative thermal oxidizer:;
Compared with the catalytic combustion and regenerative thermal oxidation furnace,; recuperative thermal oxidizer investment is less .; Recuperative thermal oxidizer system can be designed for the entire incineration system as well as the new air system,; which is more suitable for production characteristics of coating units for building materials plate.;
| Tipo de queima | Sistema de tratamento | eficiência | Vantagem | Desvantagem | |
| Eficiência do tratamento | Taxa de reciclagem de calor | ||||
| Incineração em alta temperatura | Regenerativo-RTO | 99 % | 80-97 % | Good product quality,; low energy consumption,; low cost in operational and minimum maintenance | O investimento inicial é um pouco mais alto |
| Recuperação-RTO | 98 % | 40-70 % | When adopt full incinerating design,; the energy consumption is low | High temperature joint interface is easy to broken,; maintenance cost is high | |
| Incineração em baixa temperatura | Catalisador-RCO | 98 % | 70-85 % | Low investment,; low energy consumption | VOC concentration has to be controlled strictly,; catalyst need to be changed regularly |
| Absorção de carbono ativo | 90 % | Lower investment,; self aggregation waste gas can be treated | Treatment efficiency is low,; activated carbon particle need to be replaced regularly | ||
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Recuperative Thermal Oxidizer,; recuperative Thermal Oxidizer,; recuperative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO
Endereço: 8 floor, E1, Pinwei building, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang, China
Tipo de negócio: Fabricante/fábrica, empresa comercial
Gama de negócios: Eletroeletrônicos, equipamentos e componentes industriais, máquinas de fabricação e processamento, metalurgia, minerais e energia
Certificação do sistema de gerenciamento: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Principais produtos: Rto, linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, faca de ar, peças sobressalentes para linha de processamento, revestidor, equipamentos independentes, rolo de pia, projeto de renovação, soprador
Apresentação da empresa: A ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd é uma próspera empresa de alta tecnologia, localizada na Área de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Tecnológico de ZheJiang (BDA). Seguindo o conceito de realista, inovadora, focada e eficiente, nossa empresa atende principalmente ao setor de tratamento de gases residuais (VOCs) e a equipamentos metalúrgicos da China e até mesmo do mundo todo. Possuímos tecnologia avançada e vasta experiência em projetos de tratamento de gases residuais de VOCs, cuja referência foi aplicada com sucesso no setor de revestimento, borracha, eletrônicos, impressão, etc. Também temos anos de acúmulo de tecnologia na pesquisa e fabricação de linhas de processamento de aço plano e temos quase 100 exemplos de aplicação.
Nossa empresa tem como foco a pesquisa, o projeto, a fabricação, a instalação e o comissionamento do sistema de tratamento de gás residual orgânico de VOCs e o projeto de renovação e atualização para economia de energia e proteção ambiental da linha de processamento de aço plano. Podemos oferecer aos clientes soluções completas para proteção ambiental, economia de energia, melhoria da qualidade do produto e outros aspectos.
Também estamos envolvidos em várias peças sobressalentes e equipamentos independentes para a linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, linha de decapagem, como rolo, acoplador, trocador de calor, recuperador, faca de ar, soprador, soldador, nivelador de tensão, passe de pele, junta de expansão, tesoura, juntadeira, costurador, queimador, tubo radiante, motor de engrenagem, redutor, etc.
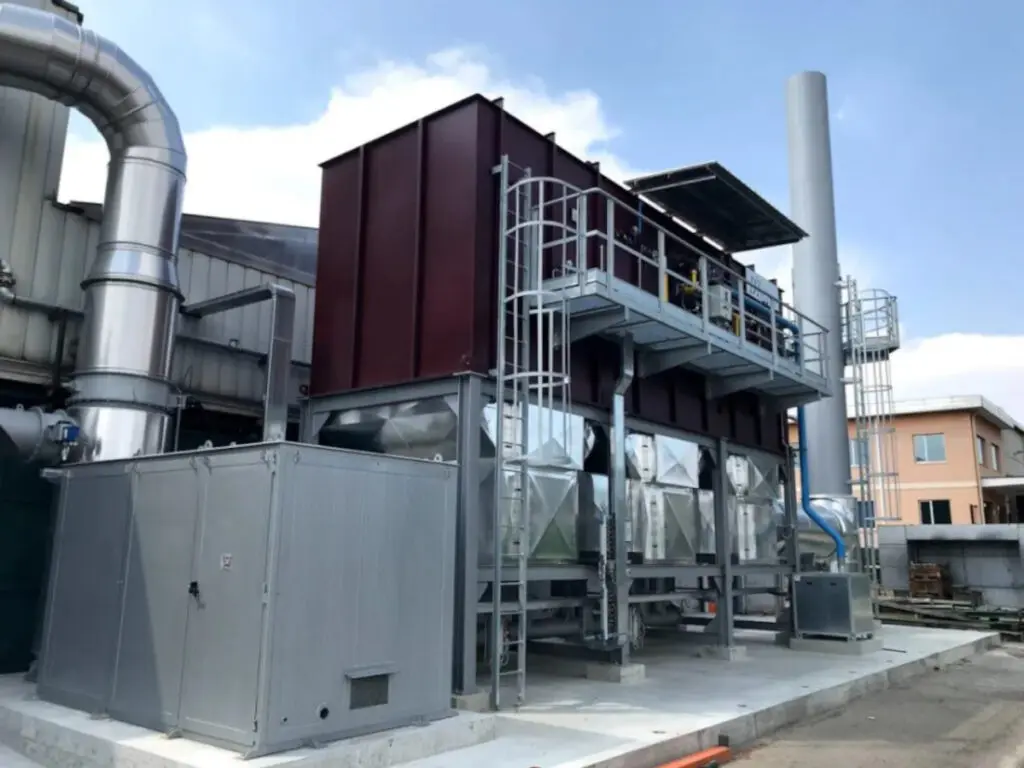

What is the role of heat recovery in a regenerative thermal oxidizer?
Heat recovery plays a crucial role in the operation of a regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) by improving its energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. The primary function of heat recovery in an RTO is to capture and transfer heat from the treated exhaust gases to the incoming untreated gases, minimizing the need for additional external heating.
Here’s a closer look at the role of heat recovery in an RTO:
- Eficiência energética: RTOs are designed to achieve high thermal efficiency by utilizing the heat recovery principle. The heat recovery system consists of heat exchangers or beds filled with ceramic media, such as structured ceramic blocks or random ceramic saddles. These beds alternate between the exhaust gas flow and the incoming untreated gas flow.
- Heat Transfer Process: During operation, the hot exhaust gases from the industrial process flow through one bed of the heat exchanger, transferring heat to the ceramic media. The media absorbs the heat, and the temperature of the exhaust gases decreases. Simultaneously, the cooler incoming untreated gas flows through the other bed, where it absorbs the heat stored in the media, preheating the gas before it enters the combustion chamber.
- Bed Switching: The direction of gas flow through the beds is periodically switched using valves or dampers. This switching operation allows the RTO to alternate between different beds, ensuring continuous heat recovery and thermal oxidation of the pollutants. By efficiently recovering and reusing heat from the exhaust gases, the RTO reduces the amount of external fuel needed to maintain the required operating temperature.
- Reduction in Fuel Consumption: The heat recovery mechanism in an RTO significantly reduces the fuel consumption compared to other types of oxidizers. The preheating of the incoming untreated gas stream reduces the energy required to raise the temperature of the gas to the combustion temperature, resulting in lower fuel usage and operational costs.
- Economic and Environmental Benefits: Heat recovery in RTOs offers economic benefits by reducing energy costs and improving the overall sustainability of the facility. By minimizing fuel consumption, heat recovery contributes to a lower carbon footprint and helps meet environmental goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the combustion process.
The effectiveness of heat recovery in an RTO depends on factors such as the design of the heat exchanger, the choice of ceramic media, the flow rates of the exhaust gases and incoming untreated gas, and the temperature differential between the two streams. Proper sizing and optimization of the heat recovery system are essential to ensure efficient heat transfer and maximize energy savings.
Overall, heat recovery is a key component in the design of an RTO, allowing for improved energy efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and environmental sustainability.
How do regenerative thermal oxidizers compare to biofilters in terms of performance?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) and biofilters are both widely used technologies for the treatment of air pollutants, but they differ in their operating principles and performance characteristics. Here’s a comparison of RTOs and biofilters in terms of their performance:
| Performance Aspect | Oxidadores térmicos regenerativos (RTOs) | Biofilters |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Removal Efficiency | RTOs are highly efficient in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). They can achieve destruction efficiencies above 95% for these pollutants. | Biofilters also have the potential to achieve high removal efficiencies for certain VOCs and odorous compounds. However, their performance can vary depending on the specific contaminants and the microbial activity in the biofilter. |
| Aplicabilidade | RTOs are versatile and can handle a wide range of pollutants, including VOCs, HAPs, and odorous compounds. They are well-suited for high flow rates and high pollutant concentrations. | Biofilters are particularly effective in treating odorous compounds and certain VOCs. They are commonly used in applications such as wastewater treatment facilities, composting operations, and agricultural facilities. |
| Energy Consumption | RTOs require a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain high operating temperatures for oxidation. They rely on fuel combustion or external heat sources for the thermal energy needed. | Biofilters are considered low energy consumption systems as they rely on the natural biological activity of microorganisms to break down pollutants. They generally do not require external heating or fuel consumption. |
| Manutenção | RTOs typically require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure proper operation. This includes inspections, cleaning of heat exchange media, and potential repairs or replacements of components. | Biofilters require periodic maintenance to optimize their performance. This may involve monitoring and adjusting moisture levels, controlling temperature, and occasionally replacing the filter media or adding microbial inoculants. |
| Capital and Operating Costs | RTOs generally have higher capital costs compared to biofilters due to their complex design, specialized materials, and energy-intensive operation. Operating costs include fuel consumption or electricity for heating. | Biofilters generally have lower capital costs compared to RTOs. They are simpler in design and do not require fuel consumption. However, operating costs may include periodic replacement of filter media and potential odor control measures. |
It is important to note that the selection of the appropriate technology depends on various factors such as the specific pollutants to be treated, process conditions, regulatory requirements, and site-specific considerations. Consulting with environmental engineers or air pollution control experts can help determine the most suitable technology for a particular application.
In summary, RTOs and biofilters offer different performance characteristics, with RTOs excelling in high removal efficiencies, versatility, and suitability for high-flow and high-concentration applications, while biofilters are effective for odorous compounds, have low energy consumption, and generally lower capital costs.
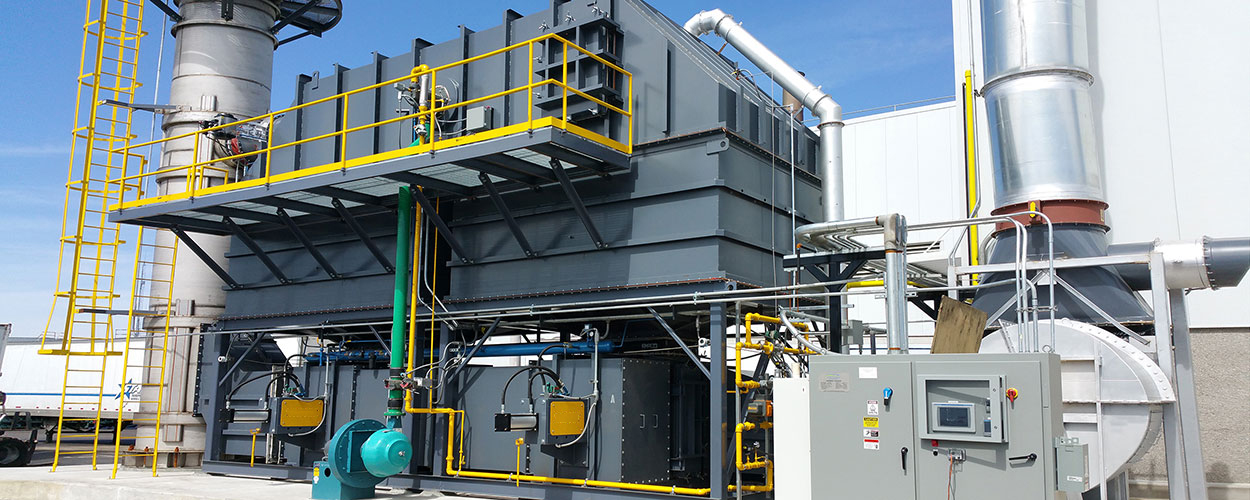

What is a regenerative thermal oxidizer?
A regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) is an advanced air pollution control device used in industrial applications to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), and other airborne contaminants from exhaust gases. It operates by using high temperatures to thermally decompose or oxidize the pollutants, converting them into less harmful byproducts.
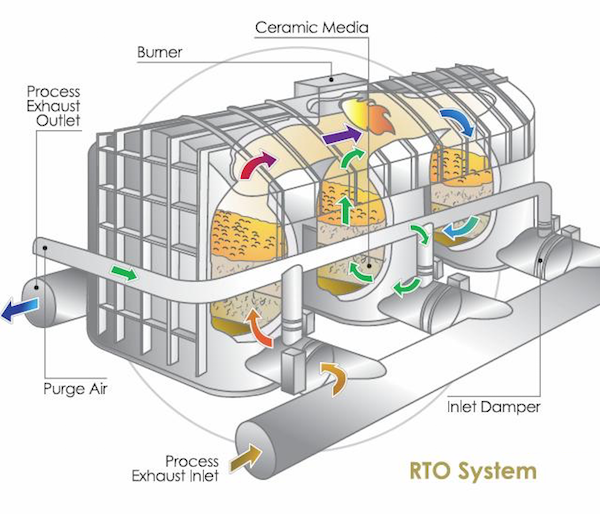
Como funciona um oxidante térmico regenerativo?
An RTO consists of several key components and operates through a cyclical process:
1. Pleno de entrada: Os gases de escape contendo poluentes entram no RTO através do plenum de admissão.
2. Leitos de troca de calor: O RTO contém vários leitos de trocadores de calor preenchidos com meios de armazenamento de calor, tipicamente materiais cerâmicos ou empacotamento estruturado. Os leitos de trocadores de calor são dispostos em pares.
3. Válvulas de controle de fluxo: As válvulas de controle de fluxo direcionam o fluxo de ar e controlam a direção dos gases de escape através do RTO.
4. Câmara de combustão: Os gases de exaustão, agora direcionados para a câmara de combustão, são aquecidos a uma alta temperatura, tipicamente entre 1400°F (760°C) e 1600°F (870°C). Essa faixa de temperatura garante oxidação térmica efetiva dos poluentes.
5. Destruição de COV: A alta temperatura na câmara de combustão faz com que os VOCs e outros contaminantes reajam com o oxigênio, resultando em sua decomposição térmica ou oxidação. Esse processo decompõe os poluentes em vapor de água, dióxido de carbono e outros gases inofensivos.
6. Recuperação de calor: Os gases quentes e purificados que saem da câmara de combustão passam pelo plenum de saída e fluem pelos leitos do trocador de calor que estão na fase oposta de operação. O meio de armazenamento de calor nos leitos absorve o calor dos gases de saída, o que pré-aquece os gases de exaustão de entrada.
7. Troca de ciclo: Após um intervalo de tempo específico, as válvulas de controle de fluxo trocam a direção do fluxo de ar, permitindo que os leitos do trocador de calor que estavam pré-aquecendo os gases de entrada agora recebam os gases quentes da câmara de combustão. O ciclo então se repete, garantindo uma operação contínua e eficiente.
Advantages of regenerative thermal oxidizers:
Os RTOs oferecem diversas vantagens no controle da poluição do ar industrial:
1. Alta eficiência: Os RTOs podem atingir altas eficiências de destruição, normalmente acima de 95%, removendo efetivamente uma ampla gama de poluentes.
2. Recuperação de energia: O mecanismo de recuperação de calor em RTOs permite economias significativas de energia. O pré-aquecimento dos gases de entrada reduz o consumo de combustível necessário para a combustão, tornando os RTOs energeticamente eficientes.
3. Custo-efetividade: Embora o investimento de capital inicial para um RTO possa ser significativo, a economia de custos operacionais a longo prazo por meio da recuperação de energia e altas eficiências de destruição o tornam uma solução econômica ao longo da vida útil do sistema.
4. Conformidade ambiental: Os RTOs são projetados para atender a regulamentações rigorosas de emissões e ajudar as indústrias a cumprir os padrões e licenças de qualidade do ar.
5. Versatilidade: Os RTOs podem lidar com uma ampla gama de volumes de exaustão de processo e concentrações de poluentes, tornando-os adequados para diversas aplicações industriais.
Overall, regenerative thermal oxidizers are highly efficient and effective air pollution control devices widely used in industries to minimize emissions and ensure environmental compliance.

editor by CX 2024-04-08
