Basic Info.
Model NO.
RTO
Processing Methods
Combustion
Pullution Sources
Air Pollution Control
Trademark
RUIMA
Origin
China
HS Code
84213990
Product Description
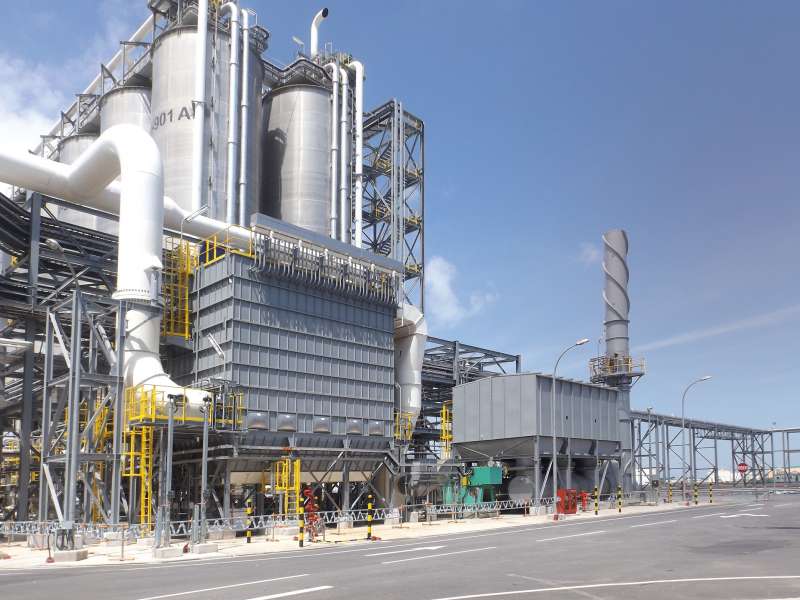
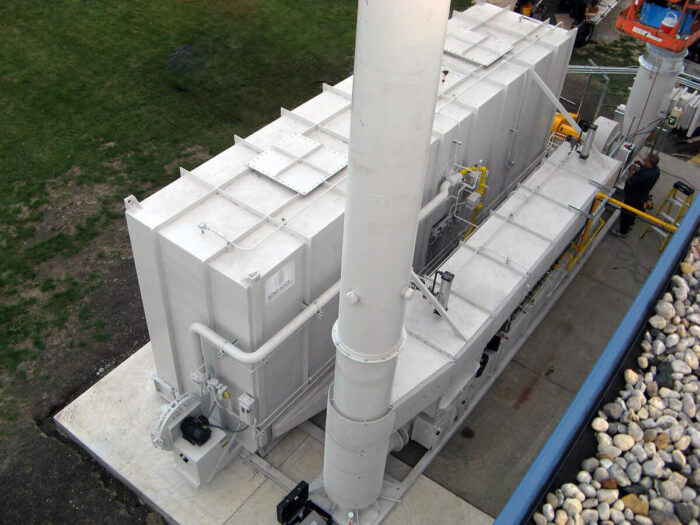
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO);
The most widely used oxidation technique nowadays for
VOC emission reduction,; suitable for treating a wide range of solvents and processes.; Depending on air volume and required purification efficiency,; a RTO comes with 2,; 3,; 5 or 10 chambers.;
장점
Wide range of VOC’s to be treated
Low maintenance cost
High Thermal Efficiency
Does not generate any waste
Adaptable for small,; medium and large air flows
Heat Recovery via bypass if VOCs concentration exceed the auto-thermal point
Auto-thermal and Heat Recovery:;
Thermal Efficiency > 95%
Auto-thermal point at 1.;2 – 1.;7 mgC/Nm3
Air flow range from 2,; 000 up to 200,; 000m3/h
High VOC’s destruction
The purification efficiency is normally in excess of 99%
Address: No 3 North Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Road, Xihu (West Lake) Dis., HangZhou, ZheJiang , China
Business Type: Manufacturer/Factory
Business Range: Manufacturing & Processing Machinery, Service
Management System Certification: ISO 14001, ISO 9001, OHSAS/ OHSMS 18001, QHSE
Main Products: Dryer, Extruder, Heater, Twin Screw Extruder, Electrochemical Corrosion Protection Equ, Screw, Mixer, Pelletizing Machine, Compressor, Pelletizer
Company Introduction: The Res. Inst of Chem. Mach of the Ministry of Chemical Industry was founded in ZheJiang in 1958, and moved to HangZhou in 1965.
The Res. Inst of Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry was founded in HangZhou in 1963.
In 1997, the Res. Inst. Of Chem. Mach of the Ministry of Chemical Industry and the Res. Inst. Of Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry were combined to become the Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry.
In 2000, the Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of the Ministry of ChemicalIndustry completed its transformation to enterprise and registered as CHINAMFG Instituteof Chemical Machinery and Automation.
Tianhua Institute has the following subordinated institutions:
Supervision and Inspection Center of the Quality of Chemical Equipments in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province
HangZhou Equipment Institute in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
Automation Institute in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhou Ruima Chemical Machinery Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhou Ruide Drying Technology Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhouLantai Plastics Machinery Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
ZheJiang Airuike Automation Technology Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
The HangZhou United Institute of Chemical Machinery and automation and the HangZhou United Institute of Petrochemical Industry Furnaces were founded by CHINAMFG Institute and the Sinopec.
Tianhua Institute has an occupation area of 80 000m2 and a total asset of 1 Yuan (RMB). The annual output value is 1 Yuan (RMB).
Tianhua Institute has about 916 employees, 75% of them are professional personnel. Among them are 23 professors, 249senior engineers, 226 engineers. 29 professors and senior engineers enjoy national special subsidy, On 5 people the title of Middle-aged and Young Specialist with Outstanding Contribution to the P. R. China are conferred

Are there any incentives or grants available for installing regenerative thermal oxidizers?
Yes, there are various incentives and grants available that can help offset the cost of installing regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) and other emission control technologies. These incentives are typically offered by government agencies at the local, regional, and national levels to promote environmental sustainability, air quality improvement, and compliance with emissions regulations. However, the availability and specific details of these incentives may vary depending on the location and the specific program.
Here are some examples of incentives and grants that may be available:
- Energy Efficiency Grants: Many government agencies and utility companies offer grants and financial incentives to encourage energy efficiency measures, including the installation of energy-efficient equipment like RTOs. These grants can help offset a portion of the installation costs and may be based on factors such as energy savings, reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, or specific environmental objectives.
- Environmental Grant Programs: Some governmental organizations or environmental foundations provide grants specifically targeted at reducing emissions and improving air quality. These grants may be available for industries or businesses that invest in emission control technologies, such as RTOs, to help them comply with regulations and improve their environmental performance.
- Tax Incentives and Credits: Certain jurisdictions offer tax incentives or credits to businesses or industries that invest in environmentally friendly technologies. These incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost of installing an RTO. Examples include tax credits for energy-efficient equipment, accelerated depreciation allowances, or exemptions from sales tax on eligible equipment purchases.
- Industry-Specific Programs: Some industries or sectors may have specific grant programs or incentives tailored to their unique environmental challenges. These programs may provide financial assistance for emission control projects, including the installation of RTOs, within those industries.
- Research and Development Funding: Government agencies or research organizations often provide funding opportunities for the development and implementation of innovative emission control technologies. Businesses or research institutions involved in developing advanced RTO designs or improving RTO efficiency may be eligible for research grants or funding support.
To explore the availability of incentives and grants for installing RTOs, it is recommended to contact local environmental agencies, energy efficiency programs, or business development organizations. These entities can provide information on specific incentive programs, eligibility criteria, application procedures, and any deadlines or limitations associated with the grants.
It’s important to note that incentive programs may change over time, and their availability may depend on factors such as funding allocations and government policies. Therefore, it is advisable to stay updated with the latest information and consult with relevant authorities to determine the current incentives available for installing RTOs.

Are regenerative thermal oxidizers suitable for controlling emissions from printing presses?
Yes, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) can be suitable for controlling emissions from printing presses. Printing presses can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants during the printing process, which need to be properly controlled to comply with environmental regulations and ensure air quality. Here are some key points regarding the suitability of RTOs for controlling emissions from printing presses:
- Emission Control: RTOs are designed to achieve high destruction efficiencies for VOCs and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). These pollutants are oxidized within the RTO at high temperatures, typically above 95% efficiency, converting them into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor. RTOs effectively control and reduce emissions from printing presses.
- Compatibility: RTOs can be integrated into the exhaust system of printing presses, capturing and treating the emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. The RTO is typically connected to the exhaust stack of the printing press, allowing the VOC-laden air to pass through the oxidizer for treatment.
- High Flow Rates: Printing presses can generate significant exhaust volumes due to the printing process. RTOs are designed to handle high flow rates and can accommodate the varying exhaust volumes of printing presses. This ensures effective treatment of emissions even during peak production periods.
- Thermal Capacity: RTOs have the thermal capacity to handle the temperature variations in printing press emissions. The printing process can result in varying exhaust temperatures, and RTOs are designed to operate effectively within a wide range of temperature conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: RTOs incorporate heat exchange systems that allow for the recovery and reuse of thermal energy. The heat exchangers within the RTO capture the heat from the outgoing exhaust gases and transfer it to the incoming process air or gas stream. This heat recovery process improves the overall energy efficiency of the system and reduces the need for additional fuel consumption.
- Compliance with Regulations: Printing press emissions are subject to regulatory requirements for air quality and emissions control. RTOs are capable of achieving the necessary destruction efficiencies and can help printing press operators comply with environmental regulations. The use of RTOs demonstrates a commitment to sustainable practices and responsible management of air emissions.
It is important to note that the specific design and configuration of the RTO, as well as the characteristics of the printing press emissions, should be considered when implementing an RTO for a printing press application. Consulting with experienced engineers or RTO manufacturers can provide valuable insights into the proper sizing, integration, and performance requirements for controlling emissions from printing presses.
In summary, RTOs are a suitable technology for controlling emissions from printing presses, providing high destruction efficiencies, compatibility with printing press exhaust systems, handling high flow rates and temperature variations, energy efficiency through heat recovery, and compliance with environmental regulations.
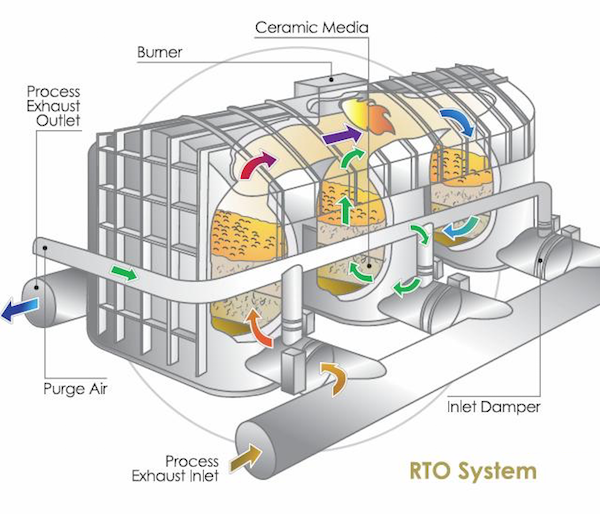
How does a regenerative thermal oxidizer work?
A regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) operates through a cyclical process that involves several key steps. Here’s a detailed explanation of how an RTO works:
1. Inlet Plenum: The exhaust gases containing pollutants enter the RTO through the inlet plenum.
2. Heat Exchanger Beds: The RTO contains multiple heat exchanger beds filled with heat storage media, typically ceramic materials or structured packing. The heat exchanger beds are arranged in pairs.
3. Flow Control Valves: Flow control valves direct the airflow and control the direction of the exhaust gases through the RTO.
4. Combustion Chamber: The exhaust gases, now directed into the combustion chamber, are heated to a high temperature, typically between 1400°F (760°C) and 1600°F (870°C). This temperature range ensures effective thermal oxidation of the pollutants.
5. VOC Destruction: The high temperature in the combustion chamber causes the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other contaminants to react with oxygen, resulting in their thermal decomposition or oxidation. This process breaks down the pollutants into water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other harmless gases.
6. Heat Recovery: The hot, purified gases leaving the combustion chamber pass through the outlet plenum and flow through the heat exchanger beds that are in the opposite phase of operation. The heat storage media in the beds absorb heat from the outgoing gases, which preheats the incoming exhaust gases.
7. Cycle Switching: After a specific time interval, the flow control valves switch the airflow direction, allowing the heat exchanger beds that were preheating the incoming gases to now receive the hot gases from the combustion chamber. The cycle then repeats, ensuring continuous and efficient operation.
Advantages of a regenerative thermal oxidizer:
RTOs offer several advantages in industrial air pollution control:
1. High Efficiency: RTOs can achieve high destruction efficiencies, typically above 95%, effectively removing a wide range of pollutants.
2. Energy Recovery: The heat recovery mechanism in RTOs allows for significant energy savings. The preheating of incoming gases reduces the fuel consumption required for combustion, making RTOs energy-efficient.
3. Cost-effectiveness: Although the initial capital investment for an RTO can be significant, the long-term operational cost savings through energy recovery and high destruction efficiencies make it a cost-effective solution over the lifespan of the system.
4. Environmental Compliance: RTOs are designed to meet stringent emissions regulations and help industries comply with air quality standards and permits.
5. Versatility: RTOs can handle a wide range of process exhaust volumes and pollutant concentrations, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Overall, a regenerative thermal oxidizer operates by utilizing heat recovery, high-temperature combustion, and cyclical flow control to effectively oxidize pollutants and achieve high destruction efficiencies while minimizing energy consumption.

editor by CX 2024-04-16
