Základní informace.
Model NO.
Úžasné RTO
Typ
Spalovna
Úspora energie
100
Snadná obsluha
100
Vysoká účinnost
100
Méně údržby
100
Ochranná známka
Bjamazing
Přepravní balíček
Zámořské dřevěné
Specifikace
180*24
Původ
Čína
Kód HS
8416100000
Popis produktu
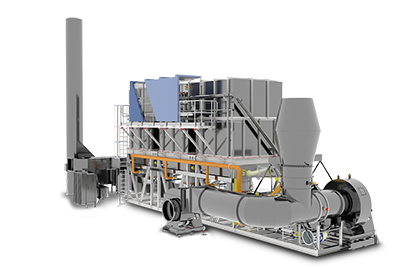
RTO
Regenerační tepelný oxidátor
V porovnání s tradičním katalytickým spalováním; přímé tepelné okysličovadlo,; RTO má přednost ve vysoké účinnosti vytápění; nízké provozní náklady; a schopnost zpracovávat odpadní plyn s nízkou koncentrací velkého toku; Když je koncentrace VOC vysoká,; lze realizovat sekundární recyklaci tepla,; což výrazně sníží provozní náklady.; Vzhledem k tomu, že RTO může předehřívat odpadní plyn o úrovně prostřednictvím keramického akumulátoru tepla,; což by mohlo způsobit, že se odpadní plyn úplně zahřeje a popraská bez mrtvého rohu (účinnost čištění > 99 %);,;které snižují NOX ve výfukových plynech;; pokud je hustota VOC > 1500 mg/Nm3; když odpadní plyn dosáhne oblasti praskání; byla zahřátá na teplotu praskání pomocí tepelného akumulátoru; hořák bude za těchto podmínek uzavřen.;
RTO lze rozdělit na typ komory a rotační typ podle rozdílu provozního režimu.; Rotační typ RTO má výhody v systémovém tlaku,; teplotní stabilita; výše investice,; atd
| RTO types | Efficiency | Pressure change (mmAq); | Size | (max);Treatment volume | |
| Treatment efficiency | Heat recycle efficiency | ||||
| Rotary type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | small(1 time); | 50000Nm3/h |
| Three chamber type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | Large (1.;5times); | 100000Nm3/h |
| Two chamber type RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | middle(1.;2times); | 100000Nm3/h |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO
Adresa: 8 patro, E1, budova Pinwei, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang, Čína
Typ podnikání: Výrobce/Továrna, Obchodní společnost
Rozsah podnikání: Elektrika a elektronika, Průmyslová zařízení a komponenty, Stroje na výrobu a zpracování, Metalurgie, Nerosty a energie
Certifikace systému managementu: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Hlavní produkty: Rto, barevná lakovací linka, galvanizační linka, vzduchový nůž, náhradní díly pro zpracovatelskou linku, nanášecí stroj, nezávislá zařízení, dřezový válec, projekt renovace, dmychadlo
Představení společnosti: ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd je prosperující hi-tech společnost se sídlem v oblasti hospodářského a technologického rozvoje ZheJiang (BDA). V souladu s konceptem realistického, inovativního, zaměřeného a efektivního naše společnost slouží především průmyslu zpracování odpadních plynů (VOC) a metalurgickým zařízením Číny a dokonce i celého světa. Máme pokročilou technologii a bohaté zkušenosti s projektem zpracování odpadních plynů VOCs, jehož reference byla úspěšně aplikována v průmyslu nátěrových hmot, pryže, elektroniky, polygrafie atd. Máme také roky technologické akumulace ve výzkumu a výrobě plochých linka na zpracování oceli a má téměř 100 příkladů použití.
Naše společnost se zaměřuje na výzkum, návrh, výrobu, instalaci a zprovoznění systému čištění organických odpadních plynů VOCs a projekt modernizace a aktualizace pro úsporu energie a ochranu životního prostředí linky na zpracování ploché oceli. Můžeme zákazníkům poskytnout kompletní řešení pro ochranu životního prostředí, úsporu energie, zlepšování kvality produktů a další aspekty.
Zabýváme se také různými náhradními díly a nezávislými zařízeními pro barevnou lakovací linku, galvanizační linku, mořicí linku, jako je válec, spojka, tepelný výměník, rekuperátor, vzduchový nůž, dmychadlo, svářečka, vyrovnávač napětí, skin pass, dilatační spára, smyk, spárovačka , sešívačka, hořák, sálavá trubice, převodový motor, reduktor atd.
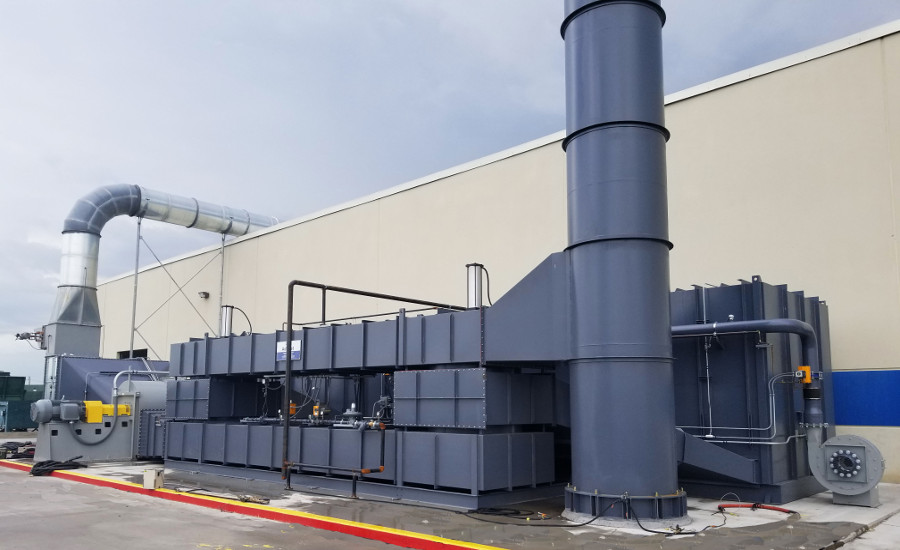

What is the difference between a regenerative thermal oxidizer and a thermal oxidizer?
A regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) and a thermal oxidizer are both types of air pollution control devices used for the treatment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. While they share the same purpose, there are distinct differences between the two technologies.
Here are the key differences between a regenerative thermal oxidizer and a thermal oxidizer:
- Operating Principle: The fundamental difference lies in the operating principle. A thermal oxidizer operates by using high temperature alone to oxidize and destroy pollutants. It typically relies on a burner or other heat sources to raise the temperature of the exhaust gases to the required level for combustion. In contrast, an RTO utilizes a regenerative heat exchanger system to preheat the incoming exhaust gases by capturing and transferring heat from the outgoing gases. This heat exchange mechanism significantly improves the overall energy efficiency of the system.
- Rekuperace tepla: Heat recovery is a distinctive feature of an RTO. The regenerative heat exchanger in an RTO allows for the recovery of a significant amount of heat from the outgoing gases. This recovered heat is then used to preheat the incoming gases, reducing the energy consumption of the system. In a typical thermal oxidizer, heat recovery is limited or absent, resulting in higher energy requirements.
- Energetická účinnost: Due to the heat recovery mechanism, RTOs are generally more energy-efficient compared to traditional thermal oxidizers. The regenerative heat exchanger in an RTO allows for thermal efficiencies of 95% or higher, meaning that a significant portion of the energy input is recovered and utilized within the system. Thermal oxidizers, on the other hand, typically have lower thermal efficiencies.
- Operating Costs: The higher energy efficiency of RTOs translates into lower operating costs over the long term. The reduced energy consumption can result in significant savings in fuel or electricity expenses compared to thermal oxidizers. However, the initial capital investment for an RTO is generally higher than that of a thermal oxidizer due to the complexity of the regenerative heat exchanger system.
- Control of Pollutant Concentrations: RTOs are better suited for handling variable pollutant concentrations compared to thermal oxidizers. The regenerative heat exchanger system in an RTO allows for better control and adjustment of operating parameters to accommodate fluctuations in pollutant concentrations. Thermal oxidizers are typically less adaptable to varying pollutant loads.
In summary, the main differences between a regenerative thermal oxidizer and a thermal oxidizer lie in the operating principle, heat recovery capabilities, energy efficiency, operating costs, and control of pollutant concentrations. RTOs offer higher energy efficiency, better control of pollutant concentrations, and lower operating costs, but they require a higher initial investment compared to traditional thermal oxidizers.
Can regenerative thermal oxidizers be remotely controlled and monitored?
Yes, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) can be remotely controlled and monitored using advanced automation and control systems. Remote control and monitoring capabilities offer several benefits in terms of operational efficiency, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Here are some key points regarding the remote control and monitoring of RTOs:
- Automation Systems: RTOs can be integrated with automation systems that enable remote control and monitoring. These systems utilize programmable logic controllers (PLCs), distributed control systems (DCS), or other similar technologies to manage and optimize the operation of the RTO.
- Remote Control: With remote control capabilities, operators can adjust and modify the operating parameters of the RTO from a central control room or even remotely through secure network connections. This allows for convenient and efficient control of the RTO, making it easier to optimize performance, adjust settings, and respond to changing process conditions.
- Remote Monitoring: Remote monitoring systems enable real-time monitoring of various parameters and performance indicators of the RTO. These systems can provide insights into the operational status, temperature profiles, gas flow rates, pressure differentials, and other critical variables. Operators can access this information remotely, allowing them to assess the system’s performance, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
- Alarms and Notifications: Remote monitoring systems can be programmed to generate alarms and notifications based on predefined conditions or thresholds. This allows operators to receive immediate alerts in case of deviations from normal operating conditions or the occurrence of any critical events. Prompt notifications facilitate timely response and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and potential risks.
- Data Logging and Analysis: Remote control and monitoring systems often include data logging capabilities, which capture historical data regarding the RTO’s operation and performance. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, evaluate efficiency, and optimize the system’s operation over time. It also helps in compliance reporting and maintenance planning.
- Integration with SCADA Systems: RTOs can be integrated with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, which provide a centralized platform for monitoring and controlling multiple processes and equipment within a facility. Integration with SCADA systems allows for a comprehensive overview of the entire operation and facilitates coordinated control and monitoring of various systems.
It is important to ensure that the remote control and monitoring systems are implemented with appropriate cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access or cyber threats. Manufacturers of RTOs often provide guidance and recommendations for implementing secure remote access to their systems.
Overall, the remote control and monitoring capabilities of RTOs enhance operational efficiency, enable proactive maintenance, and facilitate faster response times, contributing to the effective and optimized operation of the air pollution control system.
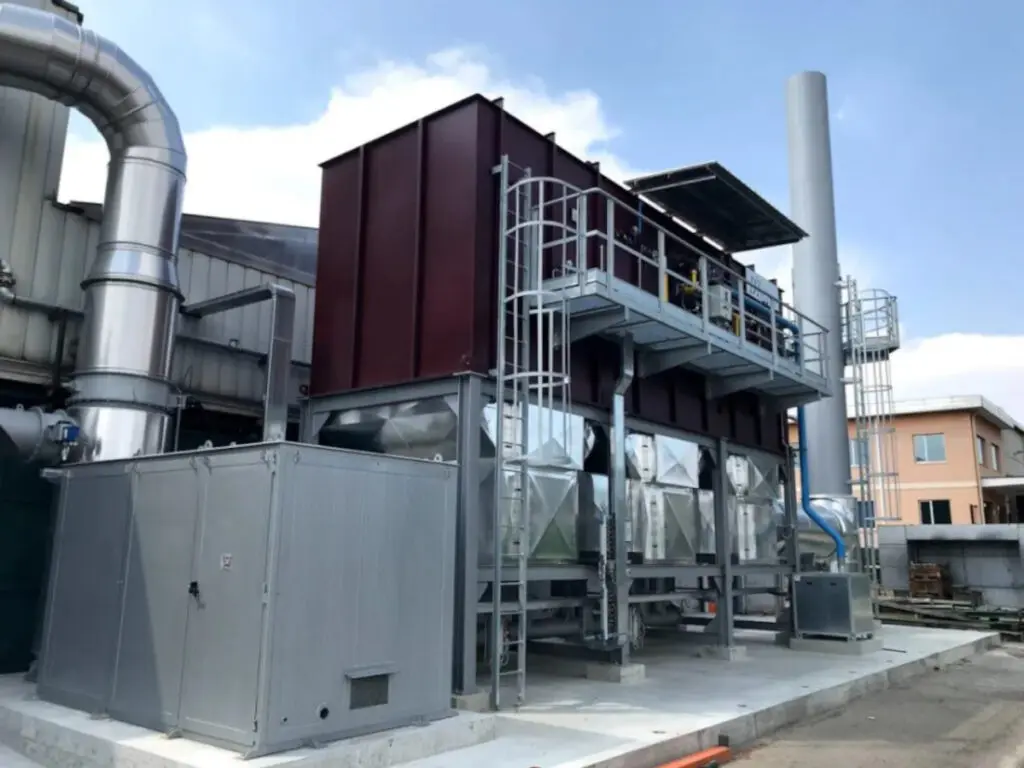

Can a regenerative thermal oxidizer handle high-volume exhaust gases?
Yes, a regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) is capable of handling high-volume exhaust gases emitted from industrial processes. RTOs are designed to handle a wide range of flow rates, including high-volume exhaust streams. Here are the reasons why RTOs are suitable for handling high-volume exhaust gases:
1. Scalability: RTOs are highly scalable and can be designed to accommodate varying exhaust gas volumes. The size and capacity of an RTO can be customized to match the specific requirements of the industrial process. This scalability allows RTOs to handle high-volume exhaust gases effectively.
2. Modular Design: RTOs often feature a modular design that allows multiple units to be installed in parallel. This modular configuration enables the treatment of large exhaust gas volumes by operating multiple RTO units simultaneously. The modular approach provides flexibility and ensures efficient handling of high-volume exhaust gases.
3. Large Heat Exchange Surface: RTOs incorporate structured ceramic media beds that provide a large heat exchange surface area. The media beds efficiently transfer heat between the incoming and outgoing gas streams, facilitating the oxidation of VOCs. The large heat exchange surface area enables RTOs to effectively handle high-volume exhaust gases while maintaining the required combustion temperature.
4. Heat Recovery: RTOs are known for their energy-efficient operation due to their heat recovery capabilities. The heat recovery system within an RTO captures and preheats the incoming process air by utilizing the heat energy from the outgoing exhaust stream. This heat recovery mechanism minimizes the energy consumption required to maintain the combustion temperature, making RTOs well-suited for handling high-volume exhaust gases without significantly increasing energy costs.
5. Effective Flow Distribution: RTOs are engineered to ensure proper flow distribution within the system. The design includes appropriate ductwork, valves, and dampers to evenly distribute the exhaust gases across the ceramic media beds. Effective flow distribution prevents preferential flow paths and ensures that all exhaust gases receive sufficient residence time for complete VOC destruction, even in high-volume exhaust gas applications.
6. Advanced Control Systems: Modern RTOs are equipped with advanced control systems that optimize the performance of the system. These control systems monitor and regulate various parameters, including temperature, airflow, and valve sequencing. The control systems adapt to the fluctuating exhaust gas volumes and maintain the required combustion temperature, ensuring efficient handling of high-volume exhaust gases.
In summary, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are capable of effectively handling high-volume exhaust gases. Their scalability, modular design, large heat exchange surface, heat recovery capabilities, effective flow distribution, and advanced control systems make RTOs well-suited for industrial processes that generate substantial exhaust gas volumes.

editor by CX 2024-03-09
