Základní informace.
Model NO.
Úžasné RTO
Typ
Spalovna
Úspora energie
100
Snadná obsluha
100
Vysoká účinnost
100
Méně údržby
100
Ochranná známka
Bjamazing
Přepravní balíček
Zámořské dřevěné
Specifikace
180*24
Původ
Čína
Kód HS
8416100000
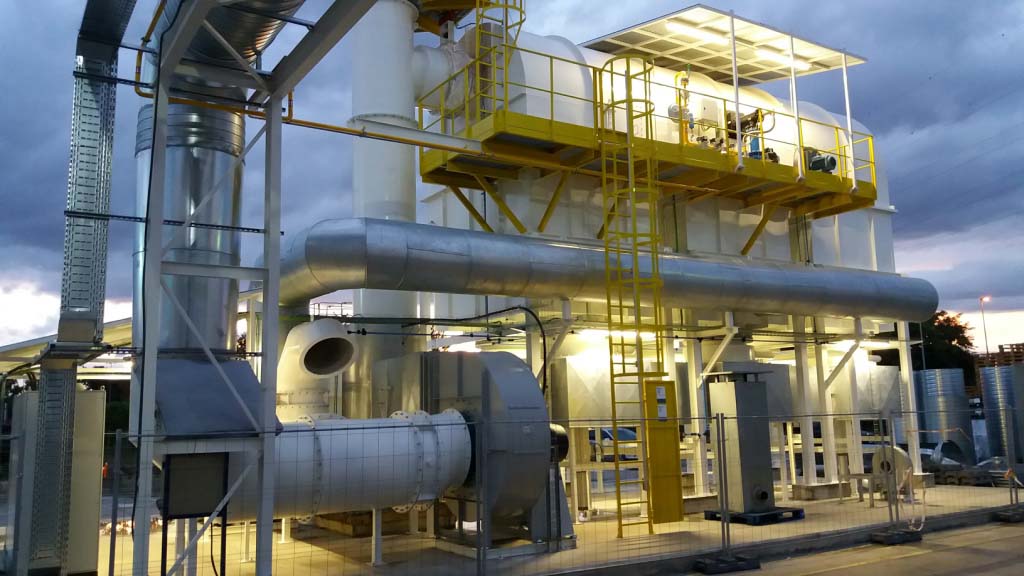
Popis produktu
RTO
Regenerační tepelný oxidátor
V porovnání s tradičním katalytickým spalováním; přímé tepelné okysličovadlo,; RTO má přednost ve vysoké účinnosti vytápění; nízké provozní náklady; a schopnost zpracovávat odpadní plyn s nízkou koncentrací velkého toku; Když je koncentrace VOC vysoká,; lze realizovat sekundární recyklaci tepla,; což výrazně sníží provozní náklady.; Vzhledem k tomu, že RTO může předehřívat odpadní plyn o úrovně prostřednictvím keramického akumulátoru tepla,; což by mohlo způsobit, že se odpadní plyn úplně zahřeje a popraská bez mrtvého rohu (účinnost čištění > 99 %);,;které snižují NOX ve výfukových plynech;; pokud je hustota VOC > 1500 mg/Nm3; když odpadní plyn dosáhne oblasti praskání; byla zahřátá na teplotu praskání pomocí tepelného akumulátoru; hořák bude za těchto podmínek uzavřen.;
RTO lze rozdělit na typ komory a rotační typ podle rozdílu provozního režimu.; Rotační typ RTO má výhody v systémovém tlaku,; teplotní stabilita; výše investice,; atd
| RTO types | Efficiency | Pressure change (mmAq); | Size | (max);Treatment volume | |
| Treatment efficiency | Heat recycle efficiency | ||||
| Rotary type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | small(1 time); | 50000Nm3/h |
| Three chamber type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | Large (1.;5times); | 100000Nm3/h |
| Two chamber type RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | middle(1.;2times); | 100000Nm3/h |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO
Adresa: 8 patro, E1, budova Pinwei, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang, Čína
Typ podnikání: Výrobce/Továrna, Obchodní společnost
Rozsah podnikání: Elektrika a elektronika, Průmyslová zařízení a komponenty, Stroje na výrobu a zpracování, Metalurgie, Nerosty a energie
Certifikace systému managementu: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Hlavní produkty: Rto, barevná lakovací linka, galvanizační linka, vzduchový nůž, náhradní díly pro zpracovatelskou linku, nanášecí stroj, nezávislá zařízení, dřezový válec, projekt renovace, dmychadlo
Představení společnosti: ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd je prosperující hi-tech společnost se sídlem v oblasti hospodářského a technologického rozvoje ZheJiang (BDA). V souladu s konceptem realistického, inovativního, zaměřeného a efektivního naše společnost slouží především průmyslu zpracování odpadních plynů (VOC) a metalurgickým zařízením Číny a dokonce i celého světa. Máme pokročilou technologii a bohaté zkušenosti s projektem zpracování odpadních plynů VOCs, jehož reference byla úspěšně aplikována v průmyslu nátěrových hmot, pryže, elektroniky, polygrafie atd. Máme také roky technologické akumulace ve výzkumu a výrobě plochých linka na zpracování oceli a má téměř 100 příkladů použití.
Naše společnost se zaměřuje na výzkum, návrh, výrobu, instalaci a zprovoznění systému čištění organických odpadních plynů VOCs a projekt modernizace a aktualizace pro úsporu energie a ochranu životního prostředí linky na zpracování ploché oceli. Můžeme zákazníkům poskytnout kompletní řešení pro ochranu životního prostředí, úsporu energie, zlepšování kvality produktů a další aspekty.
Zabýváme se také různými náhradními díly a nezávislými zařízeními pro barevnou lakovací linku, galvanizační linku, mořicí linku, jako je válec, spojka, tepelný výměník, rekuperátor, vzduchový nůž, dmychadlo, svářečka, vyrovnávač napětí, skin pass, dilatační spára, smyk, spárovačka , sešívačka, hořák, sálavá trubice, převodový motor, reduktor atd.

Can a regenerative thermal oxidizer be retrofitted into an existing facility?
Yes, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) can be retrofitted into existing facilities under certain conditions. Retrofitting an RTO involves integrating the system into the existing infrastructure and process flow of the facility to control emissions from industrial processes. However, the feasibility of retrofitting an RTO depends on several factors related to the facility and the specific requirements of the application.
Here are some considerations for retrofitting an RTO into an existing facility:
- Space Availability: RTOs typically require a significant amount of physical space for installation. It’s important to assess whether the facility has adequate space to accommodate the size and layout requirements of the RTO system. This includes considering the space needed for the RTO unit itself, associated ductwork, auxiliary systems, and access for maintenance.
- Process Integration: Retrofitting an RTO involves integrating the system into the existing industrial process. This integration may require modifications to the process flow, such as rerouting ductwork, adding or modifying exhaust points, or coordinating with existing pollution control equipment. The compatibility of the RTO with the existing process and the ability to seamlessly integrate the system should be evaluated.
- Auxiliary Systems: In addition to the RTO unit, auxiliary systems may be required for effective operation and compliance. These systems can include pre-treatment equipment such as scrubbers or filters, heat recovery units, monitoring and control systems, and stack emissions monitoring equipment. The availability of space and compatibility with existing infrastructure should be considered for accommodating these auxiliary systems.
- Utility Requirements: RTOs have specific utility requirements, such as the need for natural gas or electricity for heating the combustion chamber and operating the control system. The availability and capacity of utilities at the existing facility should be assessed to ensure they can meet the demands of the RTO system.
- Structural Considerations: The structural integrity of the facility should be evaluated to determine if it can support the additional weight of the RTO and associated equipment. This assessment may involve consulting with structural engineers and considering any necessary reinforcements or modifications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Retrofitting an RTO may require obtaining permits and complying with environmental regulations. It is essential to assess the applicable regulations and ensure that the retrofit meets the necessary compliance requirements for emissions control.
It is important to consult with experienced engineering firms or RTO manufacturers who can assess the specific requirements and constraints of the facility. They can provide detailed evaluations, feasibility studies, and design recommendations for retrofitting an RTO into an existing facility. Their expertise can help ensure that the retrofit is successful, cost-effective, and compliant with environmental regulations.
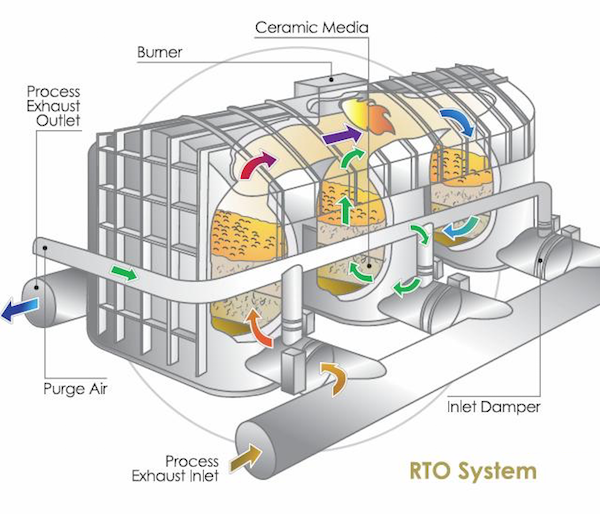
How do regenerative thermal oxidizers compare to biofilters in terms of performance?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) and biofilters are both widely used technologies for the treatment of air pollutants, but they differ in their operating principles and performance characteristics. Here’s a comparison of RTOs and biofilters in terms of their performance:
| Performance Aspect | Regenerační tepelné oxidátory (RTO) | Biofilters |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Removal Efficiency | RTOs are highly efficient in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). They can achieve destruction efficiencies above 95% for these pollutants. | Biofilters also have the potential to achieve high removal efficiencies for certain VOCs and odorous compounds. However, their performance can vary depending on the specific contaminants and the microbial activity in the biofilter. |
| Applicability | RTOs are versatile and can handle a wide range of pollutants, including VOCs, HAPs, and odorous compounds. They are well-suited for high flow rates and high pollutant concentrations. | Biofilters are particularly effective in treating odorous compounds and certain VOCs. They are commonly used in applications such as wastewater treatment facilities, composting operations, and agricultural facilities. |
| Energy Consumption | RTOs require a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain high operating temperatures for oxidation. They rely on fuel combustion or external heat sources for the thermal energy needed. | Biofilters are considered low energy consumption systems as they rely on the natural biological activity of microorganisms to break down pollutants. They generally do not require external heating or fuel consumption. |
| Maintenance | RTOs typically require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure proper operation. This includes inspections, cleaning of heat exchange media, and potential repairs or replacements of components. | Biofilters require periodic maintenance to optimize their performance. This may involve monitoring and adjusting moisture levels, controlling temperature, and occasionally replacing the filter media or adding microbial inoculants. |
| Capital and Operating Costs | RTOs generally have higher capital costs compared to biofilters due to their complex design, specialized materials, and energy-intensive operation. Operating costs include fuel consumption or electricity for heating. | Biofilters generally have lower capital costs compared to RTOs. They are simpler in design and do not require fuel consumption. However, operating costs may include periodic replacement of filter media and potential odor control measures. |
It is important to note that the selection of the appropriate technology depends on various factors such as the specific pollutants to be treated, process conditions, regulatory requirements, and site-specific considerations. Consulting with environmental engineers or air pollution control experts can help determine the most suitable technology for a particular application.
In summary, RTOs and biofilters offer different performance characteristics, with RTOs excelling in high removal efficiencies, versatility, and suitability for high-flow and high-concentration applications, while biofilters are effective for odorous compounds, have low energy consumption, and generally lower capital costs.

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers handle start-up and shutdown procedures?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) have specific procedures for start-up and shutdown to ensure safe and efficient operation. These procedures are designed to optimize the performance of the RTO and minimize any potential risks. Here is an overview of how RTOs handle start-up and shutdown:
- Start-up Procedure: During start-up, the RTO goes through a series of steps to reach its operating temperature. The start-up procedure typically involves the following stages:
- Purge Stage: The RTO is purged with clean air or an inert gas to remove any potential flammable or explosive gases that may have accumulated during the shutdown period.
- Preheat Stage: The RTO’s heat exchangers are preheated using a burner or an auxiliary heat source. This gradually increases the temperature of the heat exchange media (typically ceramic or metallic beds) and the combustion chamber.
- Heat Soak Stage: Once the heat exchangers reach a certain temperature, the RTO enters the heat soak stage. In this stage, the heat exchangers are fully heated, and the RTO operates in a self-sustaining mode, with the combustion chamber temperature being maintained primarily by the heat released from the oxidation of pollutants in the exhaust gas.
- Normal Operation: After the heat soak stage, the RTO is considered to be in normal operation mode, where it maintains the desired operating temperature and treats the exhaust gas containing pollutants.
- Shutdown Procedure: The shutdown procedure of an RTO is aimed at safely and efficiently stopping the operation of the system. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Cool Down: The RTO is gradually cooled down by reducing the flow of the exhaust gas and the supply of combustion air. This helps to prevent thermal stress on the equipment and minimize the risk of fires or other safety hazards.
- Rekuperace tepla: During the cool-down phase, the RTO may employ heat recovery techniques to capture and utilize the residual heat for other purposes, such as preheating incoming process air or water.
- Purge: Once the RTO has cooled down sufficiently, a purge cycle is initiated to remove any residual gases or contaminants from the system. This helps to ensure a clean and safe environment for maintenance activities or subsequent start-ups.
- Complete Shutdown: After the purge cycle, the RTO is considered to be in a fully shut-down state, and it can remain in this state until the next start-up is initiated.
It is important to note that the specific start-up and shutdown procedures for an RTO may vary depending on the design and manufacturer. Manufacturers typically provide detailed guidelines and instructions for operating their specific RTO models, and it is crucial to follow these guidelines to ensure safe and efficient operation.

editor by CX 2024-04-10
