معلومات اساسية.
نموذج رقم.
رتو
Processing Methods
Combustion
Pullution Sources
Air Pollution Control
العلامة التجارية
RUIMA
أصل
الصين
رمز النظام المنسق
84213990
وصف المنتج
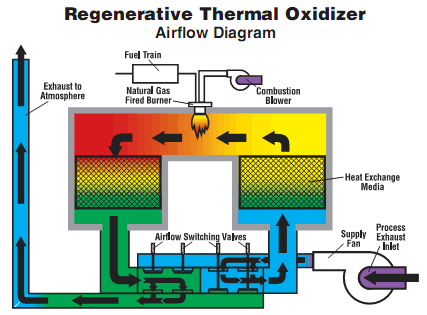
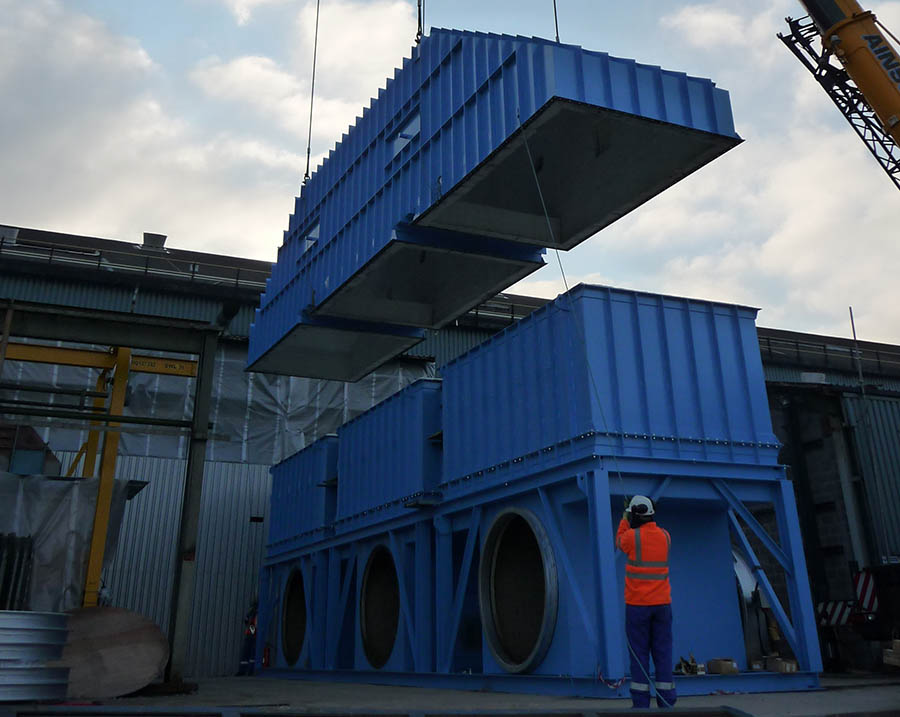
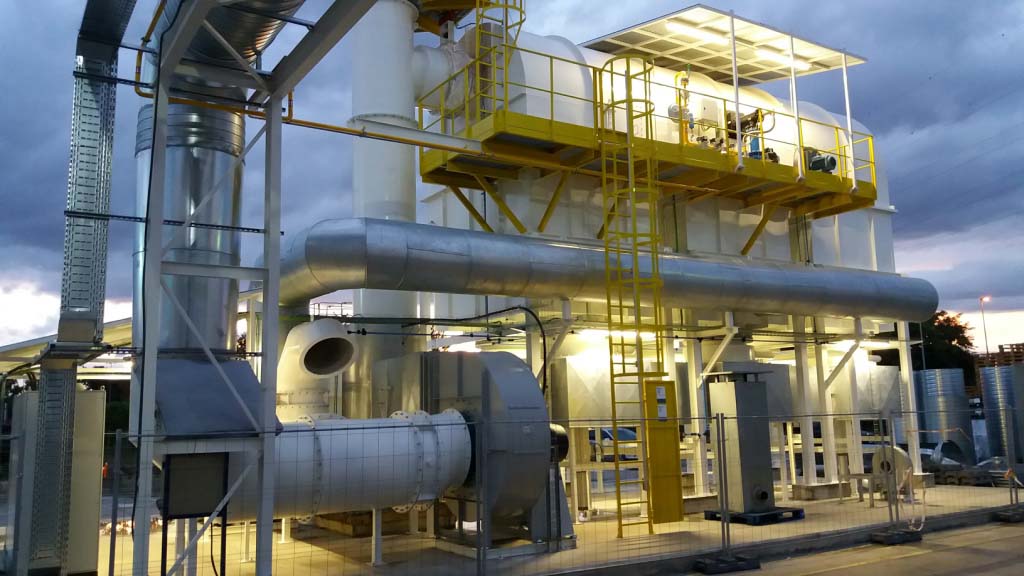
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO);
The most widely used oxidation technique nowadays for
VOC emission reduction,; suitable for treating a wide range of solvents and processes.; Depending on air volume and required purification efficiency,; a RTO comes with 2,; 3,; 5 or 10 chambers.;
المزايا
Wide range of VOC’s to be treated
Low maintenance cost
High Thermal Efficiency
Does not generate any waste
Adaptable for small,; medium and large air flows
Heat Recovery via bypass if VOCs concentration exceed the auto-thermal point
Auto-thermal and Heat Recovery:;
Thermal Efficiency > 95%
Auto-thermal point at 1.;2 – 1.;7 mgC/Nm3
Air flow range from 2,; 000 up to 200,; 000m3/h
High VOC’s destruction
The purification efficiency is normally in excess of 99%
Address: No 3 North Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Road, Xihu (West Lake) Dis., HangZhou, ZheJiang , China
نوع العمل: مصنع/شركة مصنعة
Business Range: Manufacturing & Processing Machinery, Service
Management System Certification: ISO 14001, ISO 9001, OHSAS/ OHSMS 18001, QHSE
Main Products: Dryer, Extruder, Heater, Twin Screw Extruder, Electrochemical Corrosion Protection Equ, Screw, Mixer, Pelletizing Machine, Compressor, Pelletizer
Company Introduction: The Res. Inst of Chem. Mach of the Ministry of Chemical Industry was founded in ZheJiang in 1958, and moved to HangZhou in 1965.
The Res. Inst of Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry was founded in HangZhou in 1963.
In 1997, the Res. Inst. Of Chem. Mach of the Ministry of Chemical Industry and the Res. Inst. Of Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry were combined to become the Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of the Ministry of Chemical Industry.
In 2000, the Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of the Ministry of ChemicalIndustry completed its transformation to enterprise and registered as CHINAMFG Instituteof Chemical Machinery and Automation.
Tianhua Institute has the following subordinated institutions:
Supervision and Inspection Center of the Quality of Chemical Equipments in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province
HangZhou Equipment Institute in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
Automation Institute in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhou Ruima Chemical Machinery Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhou Ruide Drying Technology Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
HangZhouLantai Plastics Machinery Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
ZheJiang Airuike Automation Technology Co Ltd in HangZhou, ZheJiang Province;
The HangZhou United Institute of Chemical Machinery and automation and the HangZhou United Institute of Petrochemical Industry Furnaces were founded by CHINAMFG Institute and the Sinopec.
Tianhua Institute has an occupation area of 80 000m2 and a total asset of 1 Yuan (RMB). The annual output value is 1 Yuan (RMB).
Tianhua Institute has about 916 employees, 75% of them are professional personnel. Among them are 23 professors, 249senior engineers, 226 engineers. 29 professors and senior engineers enjoy national special subsidy, On 5 people the title of Middle-aged and Young Specialist with Outstanding Contribution to the P. R. China are conferred
Are regenerative thermal oxidizers suitable for small-scale applications?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are primarily designed for medium to large-scale industrial applications due to their specific characteristics and operational requirements. However, their suitability for small-scale applications depends on various factors:
- Process Exhaust Volume: The exhaust volume generated by the small-scale application plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of using an RTO. RTOs are typically designed to handle high exhaust volumes, and if the exhaust volume from the small-scale application is too low, it may not be cost-effective or efficient to use an RTO.
- Capital and Operating Costs: RTOs can be expensive to purchase, install, and operate. The capital investment required for a small-scale application may not be justifiable when considering the relatively lower exhaust volumes and pollutant concentrations. Additionally, the operating costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, may outweigh the benefits for small-scale operations.
- توفر المساحة: RTOs require a significant amount of physical space for installation. Small-scale applications may have space limitations, making it challenging to accommodate the size and layout requirements of an RTO system.
- Regulatory Requirements: Small-scale applications may be subject to different regulatory requirements compared to larger industrial operations. The specific emission limits and air quality standards applicable to the small-scale application should be considered to ensure compliance. Alternative emission control technologies that are more suitable for small-scale applications, such as catalytic oxidizers or biofilters, may be available.
- Process Characteristics: The nature of the small-scale application’s exhaust stream, including the type and concentration of pollutants, can influence the choice of emission control technology. RTOs are most effective for applications with high concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). If the pollutant profile of the small-scale application is different, alternative technologies may be more appropriate.
While RTOs are generally more suitable for medium to large-scale applications, it’s important to assess the specific requirements, constraints, and cost-benefit analysis for each individual small-scale application before considering the use of an RTO. Alternative emission control technologies that are better suited for small-scale operations should also be evaluated.

كيف تتعامل المؤكسدات الحرارية المتجددة مع الاختلافات في تركيب الملوثات؟
تم تصميم المؤكسدات الحرارية المتجددة (RTOs) للتعامل مع الاختلافات في تركيبة الملوثات بشكل فعال. تُستخدم المؤكسدات الحرارية المتجددة عادةً لمعالجة المركبات العضوية المتطايرة (VOCs) والملوثات الجوية الخطرة (HAPs) المنبعثة من العمليات الصناعية المختلفة. فيما يلي بعض النقاط الرئيسية فيما يتعلق بكيفية تعامل المؤكسدات الحرارية المتجددة مع الاختلافات في تركيبة الملوثات:
- عملية الأكسدة الحرارية: تستخدم محركات RTO عملية الأكسدة الحرارية للتخلص من الملوثات. تتضمن العملية رفع درجة حرارة غاز العادم إلى مستوى تتفاعل فيه الملوثات مع الأكسجين وتتأكسد إلى ثاني أكسيد الكربون (CO2).2) وبخار الماء. تعتبر عملية الأكسدة عالية الحرارة هذه فعالة في معالجة مجموعة واسعة من الملوثات، بغض النظر عن تركيبها المحدد.
- مجموعة واسعة من التوافق مع الملوثات: تم تصميم أجهزة الاحتراق والتكرير للتعامل مع مجموعة واسعة من الملوثات، بما في ذلك المركبات العضوية المتطايرة والمركبات الهيدروكربونية الخطرة ذات التركيبات الكيميائية المتنوعة. تضمن درجات الحرارة العالية للتشغيل في أجهزة الاحتراق والتكرير، والتي تتراوح عادةً بين 1400 درجة فهرنهايت إلى 1600 درجة فهرنهايت (760 درجة مئوية إلى 870 درجة مئوية)، إمكانية أكسدة مجموعة واسعة من المركبات العضوية بشكل فعال، بغض النظر عن بنيتها الجزيئية أو تركيبها الكيميائي.
- وقت الإقامة ووقت البقاء: توفر RTOs وقت إقامة ووقت بقاء كافيين لغاز العادم داخل المؤكسد. يتم توجيه غاز العادم من خلال نظام تبادل حراري، حيث يمر عبر أسرّة وسائط سيراميكية أو وسائط تبادل حراري. تمتص أسرّة الوسائط هذه الحرارة من غرفة الاحتراق ذات درجة الحرارة العالية وتنقلها إلى غاز العادم الوارد. يضمن وقت الإقامة ووقت السكون الممتدان أن حتى الملوثات المعقدة أو الأقل تفاعلية لديها وقت اتصال كافٍ مع درجة الحرارة المرتفعة ليتم أكسدتها بشكل فعال.
- استعادة الحرارة: تتضمن محطات المعالجة الحرارية أنظمة استعادة الحرارة التي تعمل على تعظيم الكفاءة الحرارية. تعمل المبادلات الحرارية داخل محطة المعالجة الحرارية على التقاط ونقل الحرارة من غاز العادم الخارج إلى تيار العملية الوارد. تساعد عملية تبادل الحرارة هذه في الحفاظ على درجات حرارة التشغيل العالية المطلوبة لتدمير الملوثات بشكل فعال مع تقليل استهلاك الطاقة للنظام. تساهم القدرة على استعادة الحرارة وإعادة استخدامها أيضًا في قدرة محطة المعالجة الحرارية على التعامل مع الاختلافات في تركيبة الملوثات.
- أنظمة التحكم المتقدمة: تستخدم محطات المعالجة الحرارية أنظمة تحكم متقدمة لمراقبة وتحسين عملية الأكسدة. تراقب أنظمة التحكم هذه باستمرار معلمات مثل درجة الحرارة ومعدلات التدفق وتركيزات الملوثات. من خلال ضبط ظروف التشغيل استجابة للتغيرات في تركيبة الملوثات، تضمن أنظمة التحكم الأداء الأمثل وتحافظ على كفاءة تدمير عالية.
باختصار، تتعامل محطات المعالجة الحرارية مع الاختلافات في تركيبة الملوثات من خلال استخدام عملية الأكسدة الحرارية، واستيعاب مجموعة واسعة من الملوثات، وتوفير وقت إقامة كافٍ ووقت بقاء، ودمج أنظمة استعادة الحرارة، واستخدام أنظمة التحكم المتقدمة. تسمح هذه الميزات لمحطات المعالجة الحرارية بمعالجة الانبعاثات بتركيبات ملوثات مختلفة بفعالية، مما يضمن كفاءة تدمير عالية والامتثال للوائح البيئية.

How efficient are regenerative thermal oxidizers in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs)?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are highly efficient in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from industrial processes. Here are the reasons why RTOs are considered efficient in VOC destruction:
1. كفاءة تدمير عالية: RTOs are known for their high destruction efficiency, typically exceeding 99%. They effectively oxidize VOCs present in the industrial exhaust streams, converting them into less harmful byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. This high destruction efficiency ensures that the majority of VOCs are eliminated, resulting in cleaner emissions and compliance with environmental regulations.
2. Residence Time: RTOs provide a sufficiently long residence time for the combustion of VOCs. In the RTO chamber, the VOC-laden air is directed through a ceramic media bed, which acts as a heat sink. The VOCs are heated to the combustion temperature and react with the available oxygen, leading to their destruction. The design of RTOs ensures that the VOCs have ample time to undergo complete combustion before being released into the atmosphere.
3. Temperature Control: RTOs maintain the combustion temperature within a specific range to optimize VOC destruction. The operating temperature is carefully controlled based on factors such as the type of VOCs, their concentration, and the specific requirements of the industrial process. By controlling the temperature, RTOs ensure that the VOCs are efficiently oxidized, maximizing destruction efficiency while minimizing the formation of harmful byproducts, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx).
4. Heat Recovery: RTOs incorporate a regenerative heat recovery system, which enhances their overall energy efficiency. The system captures and preheats the incoming process air by utilizing the heat energy from the outgoing exhaust stream. This heat recovery mechanism minimizes the amount of external fuel required to sustain the combustion temperature, resulting in energy savings and cost-effectiveness. The heat recovery also helps maintain the high destruction efficiency of VOCs by providing a consistent and optimized operating temperature.
5. Catalyst Integration: In some cases, RTOs can be equipped with catalyst beds to further enhance VOC destruction efficiency. Catalysts can accelerate the oxidation process and lower the required operating temperature, improving the overall efficiency of VOC destruction. Catalyst integration is particularly beneficial for processes with lower VOC concentrations or when specific VOCs require lower temperatures for effective oxidation.
6. Compliance with Regulations: The high destruction efficiency of RTOs ensures compliance with environmental regulations governing VOC emissions. Many industrial sectors are subject to stringent air quality standards and emission limits. RTOs provide an effective solution for meeting these requirements by reliably and efficiently destroying VOCs, reducing their impact on air quality and public health.
In summary, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are highly efficient in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Their high destruction efficiency, residence time, temperature control, heat recovery capabilities, optional catalyst integration, and compliance with regulations make RTOs a preferred choice for industries seeking effective and sustainable solutions for VOC abatement.

editor by CX 2024-02-19
