Informações básicas.
Modelo NO.
RTO incrível
Tipo
Incinerador
Alta eficiência
100
Economia de energia
100
Baixa manutenção
100
Fácil operação
100
Marca registrada
Fantástico
Pacote de transporte
No exterior
Especificação
111
Origem
China
Código HS
2221111
Descrição do produto
RTO
Oxidador térmico regenerativo
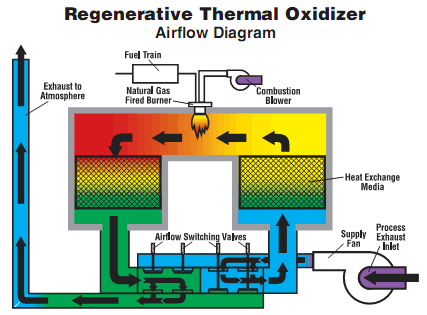
Compared with traditional catalytic combustion,; direct thermal oxidizer,; RTO has the merits of high heating efficiency,; low operation cost,; and the ability to treat large flux low concentration waste gas.; When VOCs concentration is high,; secondary heat recycle can be realized,; which will greatly reduce the operation cost.; Because RTO can preheat the waste gas by levels through ceramic heat accumulator,; which could make the waste gas to be completely heated and cracked with no dead corner(treatment efficiency>99%);,;which reduce the NOX in the Exhausting gas,; if the VOC density >1500mg/Nm3,; when the waste gas reach cracking area,; it has been heated up to cracking temperature by heat accumulator,; the burner will be closed under this condition.;
RTO can be devided into chamber type and rotary type according to difference operation mode.; Rotary type RTO has advantages in system pressure,; temperature stability,; investment amount,; etc
| Tipos de RTO | Eficiência | Mudança de pressão (mmAq); | Tamanho | (max);Treatment volume | |
| Eficiência do tratamento | Eficiência de reciclagem de calor | ||||
| Tipo rotativo RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | pequeno (1 time); | 50000Nm3/h |
| RTO do tipo três câmaras | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | Grande (1.;5times); | 100000Nm3/h |
| Tipo de duas câmaras RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | médio (1.;2times); | 100000Nm3/h |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Chamber RTO,; Chamber RTO,; Chamber RTO
Endereço: 8 floor, E1, Pinwei building, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang, China
Tipo de negócio: Fabricante/fábrica, empresa comercial
Gama de negócios: Eletroeletrônicos, equipamentos e componentes industriais, máquinas de fabricação e processamento, metalurgia, minerais e energia
Certificação do sistema de gerenciamento: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Principais produtos: Rto, linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, faca de ar, peças sobressalentes para linha de processamento, revestidor, equipamentos independentes, rolo de pia, projeto de renovação, soprador
Apresentação da empresa: A ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd é uma próspera empresa de alta tecnologia, localizada na Área de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Tecnológico de ZheJiang (BDA). Seguindo o conceito de realista, inovadora, focada e eficiente, nossa empresa atende principalmente ao setor de tratamento de gases residuais (VOCs) e a equipamentos metalúrgicos da China e até mesmo do mundo todo. Possuímos tecnologia avançada e vasta experiência em projetos de tratamento de gases residuais de VOCs, cuja referência foi aplicada com sucesso no setor de revestimento, borracha, eletrônicos, impressão, etc. Também temos anos de acúmulo de tecnologia na pesquisa e fabricação de linhas de processamento de aço plano e temos quase 100 exemplos de aplicação.
Nossa empresa tem como foco a pesquisa, o projeto, a fabricação, a instalação e o comissionamento do sistema de tratamento de gás residual orgânico de VOCs e o projeto de renovação e atualização para economia de energia e proteção ambiental da linha de processamento de aço plano. Podemos oferecer aos clientes soluções completas para proteção ambiental, economia de energia, melhoria da qualidade do produto e outros aspectos.
Também estamos envolvidos em várias peças sobressalentes e equipamentos independentes para a linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, linha de decapagem, como rolo, acoplador, trocador de calor, recuperador, faca de ar, soprador, soldador, nivelador de tensão, passe de pele, junta de expansão, tesoura, juntadeira, costurador, queimador, tubo radiante, motor de engrenagem, redutor, etc.
Are regenerative thermal oxidizers suitable for small-scale applications?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are primarily designed for medium to large-scale industrial applications due to their specific characteristics and operational requirements. However, their suitability for small-scale applications depends on various factors:
- Process Exhaust Volume: The exhaust volume generated by the small-scale application plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of using an RTO. RTOs are typically designed to handle high exhaust volumes, and if the exhaust volume from the small-scale application is too low, it may not be cost-effective or efficient to use an RTO.
- Capital and Operating Costs: RTOs can be expensive to purchase, install, and operate. The capital investment required for a small-scale application may not be justifiable when considering the relatively lower exhaust volumes and pollutant concentrations. Additionally, the operating costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, may outweigh the benefits for small-scale operations.
- Disponibilidade de espaço: RTOs require a significant amount of physical space for installation. Small-scale applications may have space limitations, making it challenging to accommodate the size and layout requirements of an RTO system.
- Regulatory Requirements: Small-scale applications may be subject to different regulatory requirements compared to larger industrial operations. The specific emission limits and air quality standards applicable to the small-scale application should be considered to ensure compliance. Alternative emission control technologies that are more suitable for small-scale applications, such as catalytic oxidizers or biofilters, may be available.
- Process Characteristics: The nature of the small-scale application’s exhaust stream, including the type and concentration of pollutants, can influence the choice of emission control technology. RTOs are most effective for applications with high concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). If the pollutant profile of the small-scale application is different, alternative technologies may be more appropriate.
While RTOs are generally more suitable for medium to large-scale applications, it’s important to assess the specific requirements, constraints, and cost-benefit analysis for each individual small-scale application before considering the use of an RTO. Alternative emission control technologies that are better suited for small-scale operations should also be evaluated.

What are the typical construction materials used in regenerative thermal oxidizers?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are constructed using various materials that can withstand the high temperatures, corrosive environments, and mechanical stresses encountered during operation. The choice of materials depends on factors such as the specific design, process conditions, and the types of pollutants being treated. Here are some typical construction materials used in RTOs:
- Heat Exchangers: The heat exchangers in RTOs are responsible for transferring heat from the outgoing exhaust gas to the incoming process air or gas stream. The construction materials for heat exchangers often include:
- Ceramic Media: RTOs commonly use structured ceramic media, such as ceramic monoliths or ceramic saddles. These materials have excellent thermal properties, high resistance to thermal shock, and good chemical resistance. Ceramic media provide a large surface area for efficient heat transfer.
- Metallic Media: Some RTO designs may incorporate metallic heat exchangers made from alloys such as stainless steel or other heat-resistant metals. Metallic media offer robustness and durability, particularly in applications with high mechanical stresses or corrosive environments.
- Combustion Chamber: The combustion chamber of an RTO is where the oxidation of pollutants takes place. The construction materials for the combustion chamber should be able to withstand the high temperatures and corrosive conditions. Commonly used materials include:
- Refractory Lining: RTOs often have refractory lining in the combustion chamber to provide thermal insulation and protection. Refractory materials, such as high-alumina or silicon carbide, are chosen for their high-temperature resistance and chemical stability.
- Steel or Alloys: The structural components of the combustion chamber, such as the walls, roof, and floor, are typically made of steel or heat-resistant alloys. These materials offer strength and stability while withstanding the high temperatures and corrosive gases.
- Ductwork and Piping: The ductwork and piping in an RTO transport the exhaust gas, process air, and auxiliary gases. The materials used for ductwork and piping depend on the specific requirements, but commonly used materials include:
- Mild Steel: Mild steel is often used for ductwork and piping in less corrosive environments. It provides strength and cost-effectiveness.
- Stainless Steel: In applications where corrosion resistance is crucial, stainless steel, such as 304 or 316 grades, may be used. Stainless steel offers excellent resistance to many corrosive gases and environments.
- Corrosion-Resistant Alloys: In highly corrosive environments, corrosion-resistant alloys like Hastelloy or Inconel may be employed. These materials provide exceptional resistance to a wide range of corrosive chemicals and gases.
- Insulation: Insulation materials are used to minimize heat loss from the RTO and ensure energy efficiency. Common insulation materials include:
- Ceramic Fiber: Ceramic fiber insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and low thermal conductivity. It is often used in RTOs to reduce heat loss and improve overall energy efficiency.
- Mineral Wool: Mineral wool insulation provides good thermal insulation and sound absorption properties. It is commonly used in RTOs to reduce heat loss and enhance safety.
It is important to note that the specific materials used in RTO construction may vary depending on factors such as the process requirements, temperature range, and corrosive nature of the gases being treated. Manufacturers of RTOs typically select appropriate materials based on their expertise and the specific application.

Como os oxidantes térmicos regenerativos lidam com os procedimentos de inicialização e desligamento?
Os oxidadores térmicos regenerativos (RTOs) têm procedimentos específicos para inicialização e desligamento a fim de garantir uma operação segura e eficiente. Esses procedimentos são projetados para otimizar o desempenho do RTO e minimizar os possíveis riscos. Aqui está uma visão geral de como os RTOs lidam com a partida e o desligamento:
- Procedimento de inicialização: Durante a inicialização, o RTO passa por uma série de etapas para atingir a temperatura operacional. O procedimento de inicialização normalmente envolve os seguintes estágios:
- Fase de purga: A RTO é purgada com ar limpo ou com um gás inerte para remover qualquer gás potencialmente inflamável ou explosivo que possa ter se acumulado durante o período de desligamento.
- Estágio de pré-aquecimento: Os trocadores de calor do RTO são pré-aquecidos usando um queimador ou uma fonte de calor auxiliar. Isso aumenta gradualmente a temperatura do meio de troca de calor (normalmente leitos cerâmicos ou metálicos) e da câmara de combustão.
- Estágio de imersão em calor: Quando os trocadores de calor atingem uma determinada temperatura, o RTO entra no estágio de imersão em calor. Nesse estágio, os trocadores de calor são totalmente aquecidos e o RTO opera em um modo autossustentável, com a temperatura da câmara de combustão sendo mantida principalmente pelo calor liberado pela oxidação dos poluentes no gás de escape.
- Operação normal: Após o estágio de imersão em calor, considera-se que a RTO está no modo de operação normal, no qual mantém a temperatura operacional desejada e trata os gases de escape que contêm poluentes.
- Procedimento de desligamento: O procedimento de desligamento de uma RTO tem como objetivo interromper a operação do sistema de forma segura e eficiente. Normalmente, o procedimento envolve as seguintes etapas:
- Resfriamento: A RTO é resfriada gradualmente por meio da redução do fluxo do gás de escape e do fornecimento de ar de combustão. Isso ajuda a evitar o estresse térmico no equipamento e a minimizar o risco de incêndios ou outros riscos à segurança.
- Recuperação de calor: Durante a fase de resfriamento, a RTO pode empregar técnicas de recuperação de calor para capturar e utilizar o calor residual para outros fins, como o pré-aquecimento do ar ou da água do processo de entrada.
- Purga: Depois que o RTO tiver esfriado o suficiente, um ciclo de purga é iniciado para remover quaisquer gases residuais ou contaminantes do sistema. Isso ajuda a garantir um ambiente limpo e seguro para as atividades de manutenção ou para as partidas subsequentes.
- Desligamento completo: Após o ciclo de purga, a RTO é considerada em um estado de desligamento total e pode permanecer nesse estado até que a próxima inicialização seja iniciada.
É importante observar que os procedimentos específicos de inicialização e desligamento de uma RTO podem variar de acordo com o projeto e o fabricante. Os fabricantes geralmente fornecem diretrizes e instruções detalhadas para a operação de seus modelos específicos de RTO, e é fundamental seguir essas diretrizes para garantir uma operação segura e eficiente.

editor by Dream 2024-10-08
