Informações básicas.
Modelo NO.
RTO incrível
Tipo
Incinerador
Alta eficiência
100
Economia de energia
100
Baixa manutenção
100
Fácil operação
100
Marca registrada
Fantástico
Pacote de transporte
No exterior
Especificação
111
Origem
China
Código HS
2221111
Descrição do produto
RTO
Oxidador térmico regenerativo
Compared with traditional catalytic combustion,; direct thermal oxidizer,; RTO has the merits of high heating efficiency,; low operation cost,; and the ability to treat large flux low concentration waste gas.; When VOCs concentration is high,; secondary heat recycle can be realized,; which will greatly reduce the operation cost.; Because RTO can preheat the waste gas by levels through ceramic heat accumulator,; which could make the waste gas to be completely heated and cracked with no dead corner(treatment efficiency>99%);,;which reduce the NOX in the Exhausting gas,; if the VOC density >1500mg/Nm3,; when the waste gas reach cracking area,; it has been heated up to cracking temperature by heat accumulator,; the burner will be closed under this condition.;
RTO can be devided into chamber type and rotary type according to difference operation mode.; Rotary type RTO has advantages in system pressure,; temperature stability,; investment amount,; etc
| Tipos de RTO | Eficiência | Mudança de pressão (mmAq); | Tamanho | (max);Treatment volume | |
| Eficiência do tratamento | Eficiência de reciclagem de calor | ||||
| Tipo rotativo RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | pequeno (1 time); | 50000Nm3/h |
| RTO do tipo três câmaras | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | Grande (1.;5times); | 100000Nm3/h |
| Tipo de duas câmaras RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | médio (1.;2times); | 100000Nm3/h |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Rotary RTO,; Chamber RTO,; Chamber RTO,; Chamber RTO
Endereço: 8 floor, E1, Pinwei building, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang, China
Tipo de negócio: Fabricante/fábrica, empresa comercial
Gama de negócios: Eletroeletrônicos, equipamentos e componentes industriais, máquinas de fabricação e processamento, metalurgia, minerais e energia
Certificação do sistema de gerenciamento: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Principais produtos: Rto, linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, faca de ar, peças sobressalentes para linha de processamento, revestidor, equipamentos independentes, rolo de pia, projeto de renovação, soprador
Apresentação da empresa: A ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd é uma próspera empresa de alta tecnologia, localizada na Área de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Tecnológico de ZheJiang (BDA). Seguindo o conceito de realista, inovadora, focada e eficiente, nossa empresa atende principalmente ao setor de tratamento de gases residuais (VOCs) e a equipamentos metalúrgicos da China e até mesmo do mundo todo. Possuímos tecnologia avançada e vasta experiência em projetos de tratamento de gases residuais de VOCs, cuja referência foi aplicada com sucesso no setor de revestimento, borracha, eletrônicos, impressão, etc. Também temos anos de acúmulo de tecnologia na pesquisa e fabricação de linhas de processamento de aço plano e temos quase 100 exemplos de aplicação.
Nossa empresa tem como foco a pesquisa, o projeto, a fabricação, a instalação e o comissionamento do sistema de tratamento de gás residual orgânico de VOCs e o projeto de renovação e atualização para economia de energia e proteção ambiental da linha de processamento de aço plano. Podemos oferecer aos clientes soluções completas para proteção ambiental, economia de energia, melhoria da qualidade do produto e outros aspectos.
Também estamos envolvidos em várias peças sobressalentes e equipamentos independentes para a linha de revestimento colorido, linha de galvanização, linha de decapagem, como rolo, acoplador, trocador de calor, recuperador, faca de ar, soprador, soldador, nivelador de tensão, passe de pele, junta de expansão, tesoura, juntadeira, costurador, queimador, tubo radiante, motor de engrenagem, redutor, etc.

How much energy can be recovered by a regenerative thermal oxidizer?
The amount of energy that can be recovered by a regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) depends on several factors, including the design of the RTO system, the operating conditions, and the specific characteristics of the exhaust gases being treated. Generally, RTOs are known for their high energy recovery efficiency, and they can recover a significant portion of the thermal energy from the exhaust gases.
Here are some key factors that influence the energy recovery potential of an RTO:
- Heat Recovery System: The design and efficiency of the heat recovery system in the RTO significantly impact the amount of energy that can be recovered. RTOs typically use ceramic media beds or heat exchangers to capture and transfer heat between the exhaust gases and the incoming untreated gases. Well-designed heat exchangers with a large surface area and good thermal conductivity can enhance the energy recovery efficiency.
- Temperature Differential: The temperature difference between the exhaust gases and the incoming untreated gases affects the energy recovery potential. The greater the temperature differential, the higher the potential for energy recovery. RTOs operating at higher temperature differentials can recover more energy compared to those with smaller differentials.
- Flow Rates and Heat Capacity: The flow rates of the exhaust gases and incoming untreated gases, as well as their respective heat capacities, are important factors in determining the energy recovery capability. Higher flow rates and larger heat capacities result in more heat available for recovery.
- Process Specifics: The specific characteristics of the industrial process and the composition of the exhaust gases being treated can influence the energy recovery potential. For example, exhaust gases with high concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other combustible components can provide a higher energy recovery potential.
- Efficiency and System Optimization: The efficiency of the RTO system itself, including the combustion chamber, heat exchangers, and control mechanisms, also plays a role in the energy recovery. Well-maintained and optimized RTO systems can maximize the energy recovery potential.
While it is challenging to provide an exact numerical value for the energy recovery potential of an RTO, it is not uncommon for RTOs to achieve energy recovery efficiencies in the range of 90% or higher. This means that they can recover and reuse 90% or more of the thermal energy contained in the exhaust gases, significantly reducing the need for external fuel sources.
It’s important to note that the actual energy recovery achieved by an RTO will depend on the specific operating conditions, pollutant concentrations, and other factors mentioned above. Consulting with RTO manufacturers or conducting a detailed energy analysis can provide more accurate estimations of the energy recovery potential for a particular RTO system.

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers handle variations in pollutant composition?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are designed to handle variations in pollutant composition effectively. RTOs are commonly used for treating volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) emitted from various industrial processes. Here are some key points regarding how RTOs handle variations in pollutant composition:
- Thermal Oxidation Process: RTOs utilize a thermal oxidation process to eliminate pollutants. The process involves raising the temperature of the exhaust gas to a level where the pollutants react with oxygen and are oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor. This high-temperature oxidation process is effective in treating a wide range of pollutants, regardless of their specific composition.
- Wide Range of Pollutant Compatibility: RTOs are designed to handle a broad spectrum of pollutants, including VOCs and HAPs with varying chemical compositions. The high operating temperatures in the RTO, typically between 1400°F to 1600°F (760°C to 870°C), ensure that a wide range of organic compounds can be effectively oxidized, regardless of their molecular structure or chemical makeup.
- Residence Time and Dwell Time: RTOs provide sufficient residence time and dwell time for the exhaust gas within the oxidizer. The exhaust gas is directed through a heat exchange system, where it passes through ceramic media beds or heat exchange media. These media beds absorb the heat from the high-temperature combustion chamber and transfer it to the incoming exhaust gas. The extended residence time and dwell time ensure that even complex or less reactive pollutants have enough contact time with the elevated temperature to be effectively oxidized.
- Recuperação de calor: RTOs incorporate heat recovery systems that maximize thermal efficiency. The heat exchangers within the RTO capture and transfer heat from the outgoing exhaust gas to the incoming process stream. This heat exchange process helps maintain the high operating temperatures required for effective pollutant destruction while minimizing the energy consumption of the system. The ability to recover and reuse heat also contributes to the RTO’s ability to handle variations in pollutant composition.
- Advanced Control Systems: RTOs employ advanced control systems to monitor and optimize the oxidation process. These control systems continuously monitor parameters such as temperature, flow rates, and pollutant concentrations. By adjusting the operating conditions in response to variations in pollutant composition, the control systems ensure optimal performance and maintain high destruction efficiencies.
In summary, RTOs handle variations in pollutant composition by utilizing a thermal oxidation process, accommodating a wide range of pollutants, providing sufficient residence time and dwell time, incorporating heat recovery systems, and employing advanced control systems. These features allow RTOs to effectively treat emissions with different pollutant compositions, ensuring high destruction efficiencies and compliance with environmental regulations.
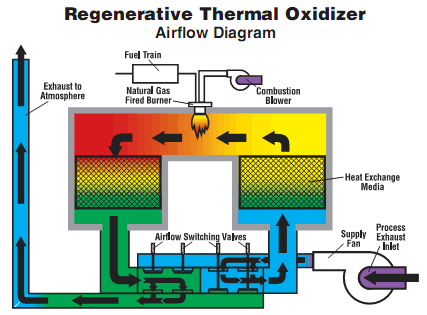
Como funciona um oxidante térmico regenerativo?
Um oxidante térmico regenerativo (RTO) é um dispositivo avançado de controle de poluição do ar que opera por meio de um processo cíclico para remover compostos orgânicos voláteis (VOCs), poluentes atmosféricos perigosos (HAPs) e outros contaminantes transportados pelo ar dos gases de exaustão. Aqui está uma explicação detalhada de como um RTO funciona:
1. Pleno de entrada: Os gases de escape contendo poluentes entram no RTO através do plenum de admissão.
2. Leitos de troca de calor: O RTO contém vários leitos de trocadores de calor preenchidos com meios de armazenamento de calor, tipicamente materiais cerâmicos ou empacotamento estruturado. Os leitos de trocadores de calor são dispostos em pares.
3. Válvulas de controle de fluxo: As válvulas de controle de fluxo direcionam o fluxo de ar e controlam a direção dos gases de escape através do RTO.
4. Câmara de combustão: Os gases de exaustão, agora direcionados para a câmara de combustão, são aquecidos a uma alta temperatura, tipicamente entre 1400°F (760°C) e 1600°F (870°C). Essa faixa de temperatura garante oxidação térmica efetiva dos poluentes.
5. Destruição de COV: A alta temperatura na câmara de combustão faz com que os VOCs e outros contaminantes reajam com o oxigênio, resultando em sua decomposição térmica ou oxidação. Esse processo decompõe os poluentes em vapor de água, dióxido de carbono e outros gases inofensivos.
6. Recuperação de calor: Os gases quentes e purificados que saem da câmara de combustão passam pelo plenum de saída e fluem pelos leitos do trocador de calor que estão na fase oposta de operação. O meio de armazenamento de calor nos leitos absorve o calor dos gases de saída, o que pré-aquece os gases de exaustão de entrada.
7. Troca de ciclo: Após um intervalo de tempo específico, as válvulas de controle de fluxo trocam a direção do fluxo de ar, permitindo que os leitos do trocador de calor que estavam pré-aquecendo os gases de entrada agora recebam os gases quentes da câmara de combustão. O ciclo então se repete, garantindo uma operação contínua e eficiente.
Vantagens de um oxidante térmico regenerativo:
Os RTOs oferecem diversas vantagens no controle da poluição do ar industrial:
1. Alta eficiência: Os RTOs podem atingir altas eficiências de destruição, normalmente acima de 95%, removendo efetivamente uma ampla gama de poluentes.
2. Recuperação de energia: O mecanismo de recuperação de calor em RTOs permite economias significativas de energia. O pré-aquecimento dos gases de entrada reduz o consumo de combustível necessário para a combustão, tornando os RTOs energeticamente eficientes.
3. Custo-efetividade: Embora o investimento de capital inicial para um RTO possa ser significativo, a economia de custos operacionais a longo prazo por meio da recuperação de energia e altas eficiências de destruição o tornam uma solução econômica ao longo da vida útil do sistema.
4. Conformidade ambiental: Os RTOs são projetados para atender a regulamentações rigorosas de emissões e ajudar as indústrias a cumprir os padrões e licenças de qualidade do ar.
5. Versatilidade: Os RTOs podem lidar com uma ampla gama de volumes de exaustão de processo e concentrações de poluentes, tornando-os adequados para diversas aplicações industriais.
No geral, um oxidante térmico regenerativo opera utilizando recuperação de calor, combustão de alta temperatura e controle de fluxo cíclico para oxidar poluentes de forma eficaz e atingir altas eficiências de destruição, minimizando o consumo de energia.

editor by CX 2024-03-11
