Maklumat Asas.
Model NO.
RTO
Kaedah Pemprosesan
Pembakaran
Punca Tarikan
Kawalan Pencemaran Udara
Tanda dagangan
RUIMA
asal usul
China
Kod HS
84213990
Penerangan Produk
Pengoksida Terma Penjanaan Semula (RTO);
Teknik pengoksidaan yang paling banyak digunakan pada masa kini untuk
Pengurangan pelepasan VOC,; sesuai untuk merawat pelbagai pelarut dan proses.; Bergantung pada isipadu udara dan kecekapan penulenan yang diperlukan,; RTO datang dengan 2,; 3,; 5 atau 10 bilik.;
Kelebihan
Pelbagai VOC untuk dirawat
Kos penyelenggaraan yang rendah
Kecekapan Terma Tinggi
Tidak menjana sebarang pembaziran
Boleh disesuaikan untuk kecil,; aliran udara sederhana dan besar
Pemulihan Haba melalui pintasan jika kepekatan VOC melebihi titik auto-terma
Auto-terma dan Pemulihan Haba:;
Kecekapan Terma > 95%
Titik auto-terma pada 1.;2 – 1.;7 mgC/Nm3
Julat aliran udara dari 2,; 000 hingga 200,; 000m3/j
Kemusnahan VOC yang tinggi
Kecekapan penulenan biasanya melebihi 99%
Address: No 3 North Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Road, Xihu (West Lake) Dis., HangZhou, ZheJiang , China
Business Type: Manufacturer/Factory
Business Range: Manufacturing & Processing Machinery, Service
Management System Certification: ISO 14001, ISO 9001, OHSAS/ OHSMS 18001, QHSE
Main Products: Dryer, Extruder, Heater, Twin Screw Extruder, Electrochemical Corrosion Protection Equ, Screw, Mixer, Pelletizing Machine, Compressor, Pelletizer
Company Introduction: The Res. Inst of Chem. Mach of the Ministry of Chemical Industry was founded in ZheJiang in 1958, and moved to HangZhou in 1965.
The Res. Inst of Automation Kementerian Industri Kimia telah diasaskan di HangZhou pada tahun 1963.
Pada tahun 1997, Res. Inst. Daripada Chem. Mach Kementerian Industri Kimia dan Res. Inst. Automasi Kementerian Industri Kimia telah digabungkan untuk menjadi Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of Kementerian Industri Kimia.
Pada tahun 2000, Res. Inst of Chemical Machinery and Automation of Ministry of ChemicalIndustry menyelesaikan transformasinya kepada perusahaan dan didaftarkan sebagai CHINAMFG Instituteof Chemical Machinery and Automation.
Institut Tianhua mempunyai institusi subordinat berikut:
Pusat Penyeliaan dan Pemeriksaan Kualiti Peralatan Kimia di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang
Institut Peralatan HangZhou di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
Institut Automasi di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
HangZhou Ruima Chemical Machinery Co Ltd di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
HangZhou Ruide Drying Technology Co Ltd di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
HangZhouLantai Plastics Machinery Co Ltd di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
ZheJiang Airuike Automation Technology Co Ltd di HangZhou, Wilayah ZheJiang;
Institut Jentera Kimia dan automasi HangZhou United dan Institut Relau Industri Petrokimia HangZhou United diasaskan oleh Institut CHINAMFG dan Sinopec.
Institut Tianhua mempunyai kawasan pekerjaan seluas 80 000m2 dan jumlah aset 1 Yuan (RMB). Nilai keluaran tahunan ialah 1 Yuan (RMB).
Institut Tianhua mempunyai kira-kira 916 pekerja, 75% daripada mereka adalah kakitangan profesional. Antaranya ialah 23 profesor, 249jurutera kanan, 226 jurutera. 29 profesor dan jurutera kanan menikmati subsidi khas negara, Kepada 5 orang gelaran Pakar Pertengahan Umur dan Muda dengan Sumbangan Cemerlang kepada RR China dianugerahkan
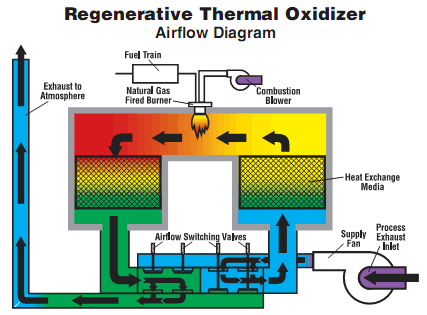
Are regenerative thermal oxidizers suitable for small-scale applications?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are primarily designed for medium to large-scale industrial applications due to their specific characteristics and operational requirements. However, their suitability for small-scale applications depends on various factors:
- Process Exhaust Volume: The exhaust volume generated by the small-scale application plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of using an RTO. RTOs are typically designed to handle high exhaust volumes, and if the exhaust volume from the small-scale application is too low, it may not be cost-effective or efficient to use an RTO.
- Capital and Operating Costs: RTOs can be expensive to purchase, install, and operate. The capital investment required for a small-scale application may not be justifiable when considering the relatively lower exhaust volumes and pollutant concentrations. Additionally, the operating costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, may outweigh the benefits for small-scale operations.
- Space Availability: RTOs require a significant amount of physical space for installation. Small-scale applications may have space limitations, making it challenging to accommodate the size and layout requirements of an RTO system.
- Regulatory Requirements: Small-scale applications may be subject to different regulatory requirements compared to larger industrial operations. The specific emission limits and air quality standards applicable to the small-scale application should be considered to ensure compliance. Alternative emission control technologies that are more suitable for small-scale applications, such as catalytic oxidizers or biofilters, may be available.
- Process Characteristics: The nature of the small-scale application’s exhaust stream, including the type and concentration of pollutants, can influence the choice of emission control technology. RTOs are most effective for applications with high concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). If the pollutant profile of the small-scale application is different, alternative technologies may be more appropriate.
While RTOs are generally more suitable for medium to large-scale applications, it’s important to assess the specific requirements, constraints, and cost-benefit analysis for each individual small-scale application before considering the use of an RTO. Alternative emission control technologies that are better suited for small-scale operations should also be evaluated.

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers handle variations in pollutant composition?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are designed to handle variations in pollutant composition effectively. RTOs are commonly used for treating volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) emitted from various industrial processes. Here are some key points regarding how RTOs handle variations in pollutant composition:
- Thermal Oxidation Process: RTOs utilize a thermal oxidation process to eliminate pollutants. The process involves raising the temperature of the exhaust gas to a level where the pollutants react with oxygen and are oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor. This high-temperature oxidation process is effective in treating a wide range of pollutants, regardless of their specific composition.
- Wide Range of Pollutant Compatibility: RTOs are designed to handle a broad spectrum of pollutants, including VOCs and HAPs with varying chemical compositions. The high operating temperatures in the RTO, typically between 1400°F to 1600°F (760°C to 870°C), ensure that a wide range of organic compounds can be effectively oxidized, regardless of their molecular structure or chemical makeup.
- Residence Time and Dwell Time: RTOs provide sufficient residence time and dwell time for the exhaust gas within the oxidizer. The exhaust gas is directed through a heat exchange system, where it passes through ceramic media beds or heat exchange media. These media beds absorb the heat from the high-temperature combustion chamber and transfer it to the incoming exhaust gas. The extended residence time and dwell time ensure that even complex or less reactive pollutants have enough contact time with the elevated temperature to be effectively oxidized.
- Pemulihan Haba: RTOs incorporate heat recovery systems that maximize thermal efficiency. The heat exchangers within the RTO capture and transfer heat from the outgoing exhaust gas to the incoming process stream. This heat exchange process helps maintain the high operating temperatures required for effective pollutant destruction while minimizing the energy consumption of the system. The ability to recover and reuse heat also contributes to the RTO’s ability to handle variations in pollutant composition.
- Advanced Control Systems: RTOs employ advanced control systems to monitor and optimize the oxidation process. These control systems continuously monitor parameters such as temperature, flow rates, and pollutant concentrations. By adjusting the operating conditions in response to variations in pollutant composition, the control systems ensure optimal performance and maintain high destruction efficiencies.
In summary, RTOs handle variations in pollutant composition by utilizing a thermal oxidation process, accommodating a wide range of pollutants, providing sufficient residence time and dwell time, incorporating heat recovery systems, and employing advanced control systems. These features allow RTOs to effectively treat emissions with different pollutant compositions, ensuring high destruction efficiencies and compliance with environmental regulations.

How efficient are regenerative thermal oxidizers in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs)?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are highly efficient in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from industrial processes. Here are the reasons why RTOs are considered efficient in VOC destruction:
1. Kecekapan Pemusnahan Tinggi: RTOs are known for their high destruction efficiency, typically exceeding 99%. They effectively oxidize VOCs present in the industrial exhaust streams, converting them into less harmful byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. This high destruction efficiency ensures that the majority of VOCs are eliminated, resulting in cleaner emissions and compliance with environmental regulations.
2. Residence Time: RTOs provide a sufficiently long residence time for the combustion of VOCs. In the RTO chamber, the VOC-laden air is directed through a ceramic media bed, which acts as a heat sink. The VOCs are heated to the combustion temperature and react with the available oxygen, leading to their destruction. The design of RTOs ensures that the VOCs have ample time to undergo complete combustion before being released into the atmosphere.
3. Temperature Control: RTOs maintain the combustion temperature within a specific range to optimize VOC destruction. The operating temperature is carefully controlled based on factors such as the type of VOCs, their concentration, and the specific requirements of the industrial process. By controlling the temperature, RTOs ensure that the VOCs are efficiently oxidized, maximizing destruction efficiency while minimizing the formation of harmful byproducts, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx).
4. Heat Recovery: RTOs incorporate a regenerative heat recovery system, which enhances their overall energy efficiency. The system captures and preheats the incoming process air by utilizing the heat energy from the outgoing exhaust stream. This heat recovery mechanism minimizes the amount of external fuel required to sustain the combustion temperature, resulting in energy savings and cost-effectiveness. The heat recovery also helps maintain the high destruction efficiency of VOCs by providing a consistent and optimized operating temperature.
5. Catalyst Integration: In some cases, RTOs can be equipped with catalyst beds to further enhance VOC destruction efficiency. Catalysts can accelerate the oxidation process and lower the required operating temperature, improving the overall efficiency of VOC destruction. Catalyst integration is particularly beneficial for processes with lower VOC concentrations or when specific VOCs require lower temperatures for effective oxidation.
6. Compliance with Regulations: The high destruction efficiency of RTOs ensures compliance with environmental regulations governing VOC emissions. Many industrial sectors are subject to stringent air quality standards and emission limits. RTOs provide an effective solution for meeting these requirements by reliably and efficiently destroying VOCs, reducing their impact on air quality and public health.
In summary, regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are highly efficient in destroying volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Their high destruction efficiency, residence time, temperature control, heat recovery capabilities, optional catalyst integration, and compliance with regulations make RTOs a preferred choice for industries seeking effective and sustainable solutions for VOC abatement.

editor by CX 2024-02-19
