基本情報
モデルNO.
驚異のRTO
タイプ
焼却炉
省エネ
100
操作が簡単
100
高効率
100
メンテナンスの軽減
100
商標
ビジャマジング
輸送パッケージ
海外木製
仕様
180*24
起源
中国
HSコード
8416100000
商品説明
RTO
再生熱酸化装置
従来の触媒燃焼と比較して、直接熱酸化装置、RTO には、加熱効率が高く、運用コストが低く、大流量の低濃度の廃ガスを処理できるという利点があります。VOC 濃度が高い場合、二次熱リサイクルが実現され、運用コストが大幅に削減されます。RTO は、セラミック蓄熱器を介して廃ガスをレベルごとに予熱できるため、死角なしで廃ガスを完全に加熱して分解できます (処理効率> 99%)。これにより、排気ガス中の NOX が削減されます。VOC 密度が >1500mg/Nm3 の場合、廃ガスが分解領域に到達すると、蓄熱器によって分解温度まで加熱されており、この状態でバーナーが閉じられます。
RTOは動作モードの違いによりチャンバー型とロータリー型に分けられます。ロータリー型RTOはシステム圧力、温度安定性、投資額などの利点があります。
| RTOタイプ | 効率性 | 圧力変化 (mmAq); | サイズ | (最大);処理量 | |
| 治療効率 | 熱再利用効率 | ||||
| ロータリー式RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | small(1 time); | 50000Nm3/時 |
| 三室式RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | 大型 (1.;5回); | 100000Nm3/時 |
| 2室式RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | middle(1.;2times); | 100000Nm3/時 |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; Thermal Oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; oxidizer,; incinerator,; incinerator,; incinerator,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; waste gas treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; VOC treatment,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO,; RTO
住所 中華人民共和国浙江省亦荘市地城西路濱偉大厦E1 8階
ビジネスタイプ メーカー/工場, 商社
事業範囲 電気・電子、産業機器・部品、製造・加工機械、冶金・鉱物・エネルギー
マネジメントシステム認証 ISO9001、ISO14001
主要製品 Rto、カラーコーティングライン、亜鉛メッキライン、エアナイフ、加工ライン用スペア、コーター、独立機器、シンクロール、改造プロジェクト、ブロワー
会社紹介 浙江驚科技有限公司は浙江経済技術開発区(BDA)に位置する盛んなハイテク企業です。現実的、革新的、集中的、効率的という理念を堅持し、主に中国及び全世界の廃ガス処理(VOCs)産業と冶金設備にサービスを提供しています。弊社はVOCs廃ガス処理プロジェクトにおいて先進的な技術と豊富な経験を持っており、コーティング、ゴム、電子、印刷などの業界への応用に成功しています。また、平鋼加工ラインの研究と製造において、長年の技術蓄積を持っており、100近くの応用例を持っています。
弊社はVOCs有機廃ガス処理システムの研究、設計、製造、据付、試運転と平鋼加工ラインの省エネと環境保護のための改造と更新プロジェクトに重点を置いています。弊社は環境保護、省エネ、製品の品質向上などの方面で、お客様に全面的な解決案を提供することができます。
また、ローラー、カプラー、熱交換器、レキュペレーター、エアナイフ、ブロワー、溶接機、テンションレベラー、スキンパス、エキスパンションジョイント、シャー、ジョインター、ステッチャー、バーナー、ラジアントチューブ、ギアモーター、減速機など、カラーコーティングライン、亜鉛メッキライン、酸洗ラインの各種スペアや独立した設備も手掛けています。
How do regenerative thermal oxidizers comply with emissions regulations?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are designed to help industries comply with emissions regulations and air quality standards. They employ several mechanisms to ensure compliance:
- Pollutant Destruction Efficiency: RTOs are engineered to achieve high destruction efficiencies for pollutants, typically exceeding 99%. This means that the vast majority of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) present in industrial exhaust streams are effectively destroyed, reducing their emissions to levels that meet or exceed regulatory requirements.
- Emission Monitoring and Reporting: RTOs often incorporate monitoring systems to measure and record various parameters, including pollutant concentrations, temperature, airflow rates, and pressure differentials. These systems enable operators to continuously monitor the performance of the RTO and ensure compliance with emissions regulations. The collected data can be used for reporting purposes to demonstrate compliance to regulatory authorities.
- Compliance with Emission Limits: RTOs are designed and operated to meet specific emission limits set by local, regional, and national regulatory agencies. These emission limits define the maximum allowable concentrations or mass emissions of pollutants that can be released into the atmosphere. RTOs are equipped with control mechanisms, such as combustion chambers, heat recovery systems, and monitoring devices, to achieve and maintain emission levels within the prescribed limits.
- Regulatory Standards and Certifications: RTOs are designed and manufactured in accordance with industry standards and guidelines, such as those set by environmental protection agencies and organizations. Compliance with these standards ensures that the RTOs meet specific criteria for performance, safety, and emissions control. Additionally, some RTO manufacturers may obtain certifications or approvals from regulatory bodies to validate their equipment’s compliance with emissions regulations.
- Periodic Inspections and Maintenance: Regular inspections, maintenance, and performance evaluations are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with emissions regulations. These activities help identify any potential issues or deviations from the required performance levels and allow for timely corrective actions. Proper maintenance practices, such as cleaning of heat exchangers, replacement of damaged components, and calibration of monitoring devices, contribute to maintaining the RTO’s effectiveness in emissions control.
It’s important to note that compliance with emissions regulations is a shared responsibility between the industry operating the RTO and the regulatory authorities overseeing environmental compliance. Industries must follow proper operating procedures, adhere to emission limits, and maintain the RTO in accordance with manufacturer’s guidelines and regulatory requirements to ensure continuous compliance.

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers compare to biofilters in terms of performance?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) and biofilters are both widely used technologies for the treatment of air pollutants, but they differ in their operating principles and performance characteristics. Here’s a comparison of RTOs and biofilters in terms of their performance:
| Performance Aspect | 再生熱酸化装置(RTO) | Biofilters |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Removal Efficiency | RTOs are highly efficient in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). They can achieve destruction efficiencies above 95% for these pollutants. | Biofilters also have the potential to achieve high removal efficiencies for certain VOCs and odorous compounds. However, their performance can vary depending on the specific contaminants and the microbial activity in the biofilter. |
| 適用性 | RTOs are versatile and can handle a wide range of pollutants, including VOCs, HAPs, and odorous compounds. They are well-suited for high flow rates and high pollutant concentrations. | Biofilters are particularly effective in treating odorous compounds and certain VOCs. They are commonly used in applications such as wastewater treatment facilities, composting operations, and agricultural facilities. |
| Energy Consumption | RTOs require a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain high operating temperatures for oxidation. They rely on fuel combustion or external heat sources for the thermal energy needed. | Biofilters are considered low energy consumption systems as they rely on the natural biological activity of microorganisms to break down pollutants. They generally do not require external heating or fuel consumption. |
| メンテナンス | RTOs typically require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure proper operation. This includes inspections, cleaning of heat exchange media, and potential repairs or replacements of components. | Biofilters require periodic maintenance to optimize their performance. This may involve monitoring and adjusting moisture levels, controlling temperature, and occasionally replacing the filter media or adding microbial inoculants. |
| Capital and Operating Costs | RTOs generally have higher capital costs compared to biofilters due to their complex design, specialized materials, and energy-intensive operation. Operating costs include fuel consumption or electricity for heating. | Biofilters generally have lower capital costs compared to RTOs. They are simpler in design and do not require fuel consumption. However, operating costs may include periodic replacement of filter media and potential odor control measures. |
It is important to note that the selection of the appropriate technology depends on various factors such as the specific pollutants to be treated, process conditions, regulatory requirements, and site-specific considerations. Consulting with environmental engineers or air pollution control experts can help determine the most suitable technology for a particular application.
In summary, RTOs and biofilters offer different performance characteristics, with RTOs excelling in high removal efficiencies, versatility, and suitability for high-flow and high-concentration applications, while biofilters are effective for odorous compounds, have low energy consumption, and generally lower capital costs.
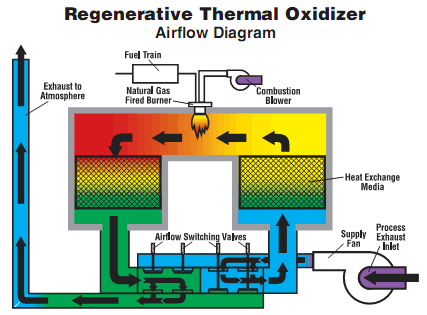
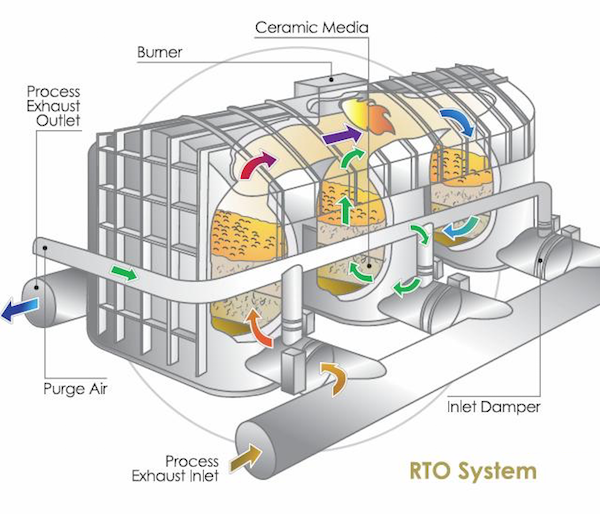
再生熱酸化装置の仕組みは?
再生熱酸化装置(RTO)は、排気ガスから揮発性有機化合物(VOC)、有害大気汚染物質(HAP)、およびその他の空気中の汚染物質を除去するために、循環プロセスを通じて動作する高度な大気汚染防止装置です。ここでは、RTOの仕組みについて詳しく説明する:
1.インレットプレナム: 汚染物質を含む排気ガスは、インレットプレナムを通ってRTOに入る。
2.熱交換器ベッド RTOは、蓄熱媒体、典型的にはセラミック材料または構造化パッキンで満たされた複数の熱交換器ベッドを含む。熱交換器ベッドは対になって配置されている。
3.流量制御バルブ: 流量制御弁は、気流を整流し、RTOを通過する排気ガスの方向を制御する。
4.燃焼室: 燃焼室に導かれた排気ガスは、通常760°C(1400°F)から870°C(1600°F)の高温に加熱される。この温度範囲により、汚染物質の効果的な熱酸化が保証される。
5.VOC破壊: 燃焼室内の高温により、VOCやその他の汚染物質が酸素と反応し、熱分解または酸化される。この過程で汚染物質は水蒸気、二酸化炭素、その他の無害なガスに分解される。
6.熱回収: 燃焼室を出た高温で浄化されたガスは、出口プレナムを通過し、作動の逆相にある熱交換器ベッドを流れる。熱交換器ベッド内の蓄熱媒体は、排出ガスから熱を吸収し、流入する排気ガスを予熱します。
7.サイクル切り替え: 特定の時間間隔が経過すると、流量制御弁が気流の方向を切り替え、流入ガスを予熱していた熱交換器床が、今度は燃焼室からの高温ガスを受け取るようにする。このサイクルが繰り返され、連続的かつ効率的な運転が保証される。
再生熱酸化装置の利点:
RTOは、産業用大気汚染防止においていくつかの利点を提供する:
1.高効率: RTOは、通常95%以上の高い破壊効率を達成し、幅広い汚染物質を効果的に除去することができる。
2.エネルギー回収: RTOの熱回収メカニズムは、大幅なエネルギー節約を可能にする。流入ガスの予熱は、燃焼に必要な燃料消費を削減し、RTOをエネルギー効率の高いものにしている。
3.費用対効果: RTOの初期設備投資は多額になる可能性があるが、エネルギー回収と高い破壊効率による長期的な運転コストの削減により、システムの寿命を通じて費用対効果の高いソリューションとなる。
4.環境コンプライアンス: RTOは、厳しい排出規制を満たし、産業界が大気質基準や許認可を遵守できるように設計されている。
5.汎用性: RTOは幅広いプロセス排気量と汚染物質濃度に対応できるため、さまざまな産業用途に適している。
全体として、再生熱酸化装置は、熱回収、高温燃焼、循環的な流量制御を利用することで、汚染物質を効果的に酸化し、エネルギー消費を最小限に抑えながら高い破壊効率を達成する。

editor by CX 2024-04-11
