Basic Info.
Model NO.
Amazing RTO
Type
Incinerator
Низький рівень обслуговування
100
Easy Operation
100
Energy Saving
100
High Efficiency
100
Trademark
Bjamazing
Transport Package
Overseas
Specification
111
Origin
China
HS Code
2221111
Product Description
RTO
Регенеративний термічний окислювач
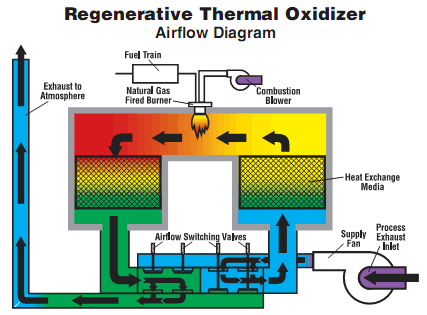
Compared with traditional catalytic combustion, direct thermal oxidizer, RTO has the merits of high heating efficiency, low operation cost, and the ability to treat large flux low concentration waste gas. When VOCs concentration is high, secondary heat recycle can be realized, which will greatly reduce the operation cost. Because RTO can preheat the waste gas by levels through ceramic heat accumulator, which could make the waste gas to be completely heated and cracked with no dead corner(treatment efficiency>99%),which reduce the NOX in the Exhausting gas, if the VOC density >1500mg/Nm3, when the waste gas reach cracking area, it has been heated up to cracking temperature by heat accumulator, the burner will be closed under this condition.
RTO can be devided into chamber type and rotary type according to difference operation mode. Rotary type RTO has advantages in system pressure, temperature stability, investment amount, etc
| RTO types | Efficiency | Pressure change (mmAq) | Size | (max)Treatment volume | |
| Treatment efficiency | Heat recycle efficiency | ||||
| Rotary type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-4 | small (1 time) | 50000Nm3/h |
| Three chamber type RTO | 99 % | 97 % | 0-10 | Large (1.5times) | 100000Nm3/h |
| Two chamber type RTO | 95 % | 95 % | 0-20 | middle (1.2times) | 100000Nm3/h |
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, Thermal Oxidizer, Thermal Oxidizer, Thermal Oxidizer, oxidizer, oxidizer, oxidizer, incinerator, incinerator, incinerator, waste gas treatment, waste gas treatment, waste gas treatment, VOC treatment, VOC treatment, VOC treatment, RTO, RTO, RTO, Rotary RTO, Rotary RTO, Rotary RTO, Chamber RTO, Chamber RTO, Chamber RTO
Address: 8 floor, E1, Pinwei building, Dishengxi road, Yizhuang, ZheJiang , China
Business Type: Manufacturer/Factory, Trading Company
Business Range: Electrical & Electronics, Industrial Equipment & Components, Manufacturing & Processing Machinery, Metallurgy, Mineral & Energy
Management System Certification: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
Main Products: Rto, Color Coating Line, Galvanizing Line, Air Knife, Spares for Processing Line, Coater, Independent Equipments, Sink Roll, Revamping Project, Blower
Company Introduction: ZheJiang Amazing Science & Technology Co., Ltd is a thriving Hi-tech company, located in ZheJiang Economic and Technological Development Area(BDA). Adhering to the concept of Realistic, Innovative, Focused and Efficient, our company mainly serve the waste gas treatment (VOCs) Industry and metallurgical equipment of China and even whole world. We have advanced technology and rich experience in VOCs waste gas treatment project, the reference of which has been successfully applied to the industry of coating, rubber, electronic, printing, etc. We also have years of technology accumulation in the research and manufacturing of flat steel processing line, and possess nearly 100 of application example.
Our company focus on the research, design, manufacturing, installation and commissioning of VOCs organic waste gas treatment system and the revamping and updating project for energy saving and environmental protection of flat steel processing line. We can provide customers the complete solutions for environmental protection, energy saving, product quality improvement and other aspects.
We are also engaged in various spares and independent equipment for color coating line, galvanizing line, pickling line, like roller, coupler, heat exchanger, recuperator, air knife, blower, welder, tension leveler, skin pass, expansion joint, shear, jointer, stitcher, burner, radiant tube, gear motor, reducer, etc.
Are regenerative thermal oxidizers suitable for small-scale applications?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are primarily designed for medium to large-scale industrial applications due to their specific characteristics and operational requirements. However, their suitability for small-scale applications depends on various factors:
- Process Exhaust Volume: The exhaust volume generated by the small-scale application plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility of using an RTO. RTOs are typically designed to handle high exhaust volumes, and if the exhaust volume from the small-scale application is too low, it may not be cost-effective or efficient to use an RTO.
- Capital and Operating Costs: RTOs can be expensive to purchase, install, and operate. The capital investment required for a small-scale application may not be justifiable when considering the relatively lower exhaust volumes and pollutant concentrations. Additionally, the operating costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, may outweigh the benefits for small-scale operations.
- Space Availability: RTOs require a significant amount of physical space for installation. Small-scale applications may have space limitations, making it challenging to accommodate the size and layout requirements of an RTO system.
- Regulatory Requirements: Small-scale applications may be subject to different regulatory requirements compared to larger industrial operations. The specific emission limits and air quality standards applicable to the small-scale application should be considered to ensure compliance. Alternative emission control technologies that are more suitable for small-scale applications, such as catalytic oxidizers or biofilters, may be available.
- Process Characteristics: The nature of the small-scale application’s exhaust stream, including the type and concentration of pollutants, can influence the choice of emission control technology. RTOs are most effective for applications with high concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). If the pollutant profile of the small-scale application is different, alternative technologies may be more appropriate.
While RTOs are generally more suitable for medium to large-scale applications, it’s important to assess the specific requirements, constraints, and cost-benefit analysis for each individual small-scale application before considering the use of an RTO. Alternative emission control technologies that are better suited for small-scale operations should also be evaluated.

How do regenerative thermal oxidizers handle particulate matter buildup in the system?
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) employ various mechanisms to handle particulate matter buildup in the system. Particulate matter, such as dust, soot, or other solid particles, can accumulate over time and potentially affect the performance and efficiency of the RTO. Here are some ways RTOs handle particulate matter buildup:
- Pre-filtration: RTOs can incorporate pre-filtration systems, such as cyclones or bag filters, to remove larger particulate matter before it enters the oxidizer. These pre-filters capture and collect the particles, preventing them from entering the RTO and reducing the potential for buildup.
- Self-Cleaning Effect: RTOs are designed to have a self-cleaning effect on the heat exchange media. During the operation of the RTO, the flow of hot exhaust gases through the media can cause the particles to burn or disintegrate, minimizing their accumulation. The high temperatures and turbulent flow help maintain clean surfaces on the media, reducing the risk of significant particulate buildup.
- Purge Cycle: RTOs typically incorporate purge cycles as part of their operation. These cycles involve introducing a small flow of clean air or gas into the system to purge any residual particulate matter. The purge air helps dislodge or burn off any particles adhering to the media, ensuring their continuous cleaning.
- Periodic Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to prevent excessive particulate matter buildup in the RTO. Maintenance activities may include inspecting and cleaning the heat exchange media, checking and replacing any worn-out gaskets or seals, and monitoring the system for any signs of particulate accumulation. Regular maintenance helps ensure optimal performance and minimizes the risk of operational issues associated with particulate matter buildup.
- Monitoring and Alarms: RTOs are equipped with monitoring systems that track various parameters such as pressure differentials, temperatures, and flow rates. These systems can detect any abnormal conditions or excessive pressure drops that may indicate particulate matter buildup. Alarms and alerts can be triggered to notify operators, prompting them to take appropriate action, such as initiating maintenance or cleaning procedures.
It is important to note that the specific strategies employed to handle particulate matter buildup may vary depending on the design and configuration of the RTO, as well as the characteristics of the particulate matter being treated. RTO manufacturers and operators should consider these factors and implement appropriate measures to ensure the effective management of particulate matter in the system.
By incorporating pre-filtration, utilizing the self-cleaning effect, implementing purge cycles, conducting regular maintenance, and employing monitoring systems, RTOs can effectively handle and mitigate particulate matter buildup, maintaining their performance and efficiency over time.

What are the key components of a regenerative thermal oxidizer?
A regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) typically consists of several key components that work together to achieve effective air pollution control. The main components of an RTO include:
- 1. Combustion Chamber: The combustion chamber is where the oxidation of the pollutants takes place. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and house the ceramic media beds that facilitate heat exchange and VOC destruction. The combustion chamber provides a controlled environment for the combustion process to occur efficiently.
- 2. Ceramic Media Beds: Ceramic media beds are the heart of an RTO. They are filled with structured ceramic materials that act as a heat sink. The media beds alternate between the inlet and outlet sides of the RTO, allowing for efficient heat transfer. As the VOC-laden air passes through the media beds, it is heated by the stored heat from the previous cycle, promoting combustion and VOC destruction.
- 3. Valves or Dampers: Valves or dampers are used to direct the airflow within the RTO. They control the flow of the process air and the direction of the exhaust gases during the different phases of operation, such as the heating, combustion, and cooling cycles. Proper valve sequencing ensures optimal heat recovery and VOC destruction efficiency.
- 4. Burner System: The burner system provides the necessary heat to raise the temperature of the incoming process air to the required combustion temperature. It typically uses natural gas or another fuel source to generate the heat energy needed for the destruction of VOCs. The burner system is designed to provide stable and controlled combustion conditions within the RTO.
- 5. Heat Recovery System: The heat recovery system enables energy efficiency in an RTO. It captures and preheats the incoming process air by utilizing the heat energy from the outgoing exhaust stream. The heat exchange occurs between the ceramic media beds, allowing for significant energy savings and reducing the overall operating costs of the RTO.
- 6. Control System: The control system of an RTO monitors and regulates the operation of various components. It ensures proper valve sequencing, temperature control, and safety interlocks. The control system optimizes the performance of the RTO, maintains the desired destruction efficiency, and provides necessary alarms and diagnostics for efficient operation and maintenance.
- 7. Stack or Exhaust System: The stack or exhaust system is responsible for releasing the treated and cleaned gases into the atmosphere. It may include a stack, ductwork, and any necessary emission monitoring equipment to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
These key components work together in a coordinated manner to provide efficient air pollution control in a regenerative thermal oxidizer. Each component plays a critical role in achieving high VOC destruction efficiency, energy recovery, and compliance with environmental standards.

editor by CX 2023-10-17
